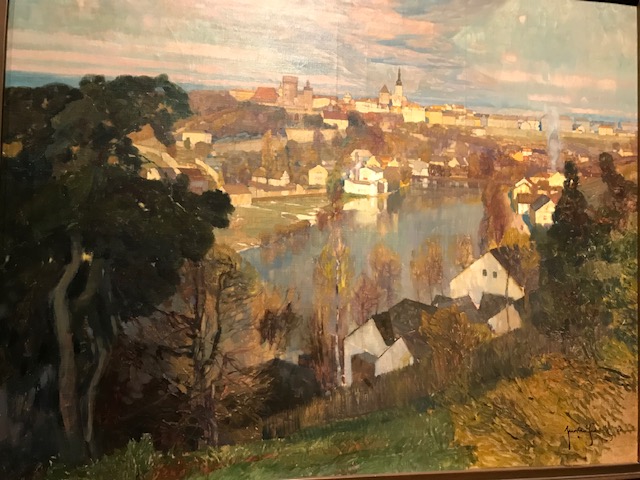
Tábor, Jaroslav Šetelík
I have always loved to visit the exhibitions at the art gallery at the Kooperativa insurance company. Never have I exited that building without learning something new about art and about myself. This time the show was called Horizons, and it brought to mind memories of childhood innocence as well as a strong sense of freedom and personal identity achieved as an adult. The featured paintings dealt with the power and magic of nature and romantic towns as well as the devastation of war. Mythological themes also punctuated some paintings. Some of the scenes evoked in me sadness, and others brought joy.
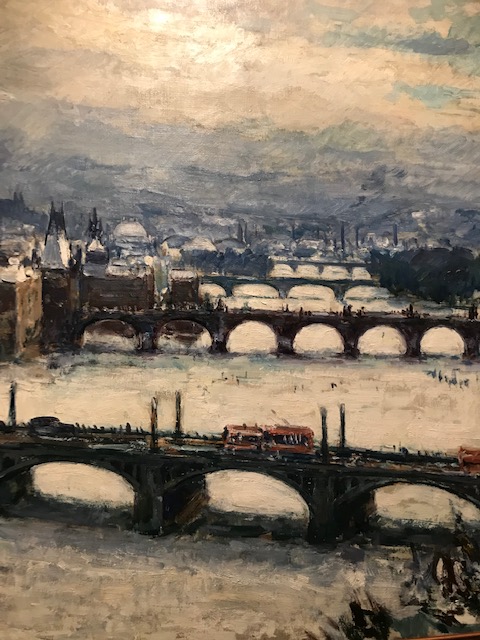

Prague Bridges, František Líbal
The townscapes were my favorites. My love of Prague drew me to the romantic and idyllic landscape “Prague Bridges” (1943) by the landscape and portrait painter František Líbal, who created vistas of the Czech capital during World War II, when he lived in Prague. Líbal studied in Germany and made trips to France and Italy while portraying cityscapes and cathedrals. He proceeded to travel throughout the Czech lands, Moravia and Slovakia, focusing on mountainous terrain. The south Bohemia native often visited the region where he was born and created many works of ponds and forests from scenery located there. After the war, he stopped creating Prague cityscapes and focused on landscapes of south Bohemia.
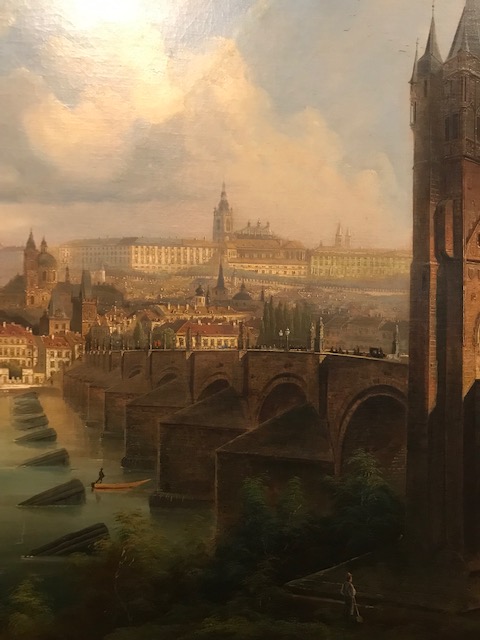
View of Charles Bridge, Ferdinand Lepié
His view of Prague brought to mind the power and magic of the capital city. He made the city appear idyllic and romantic. In the horizon of the painting, I saw the bright future that I imagined I would have when I was 21 years old, fresh out of college. I mused about my first visit to Prague in 1991, when I was initially enamored by the beauty of the city. So many decades later, I am still enthralled with the city’s beauty, and the panoramic views fill me with joy. Another painting in the exhibition that brought to mind the magic and masterful architecture in Prague was View of Charles Bridge (1861) by Ferdinand Lepié. My attention was drawn to Prague Castle in the background. I once again saw Prague imbued with historical significance and timeless beauty.
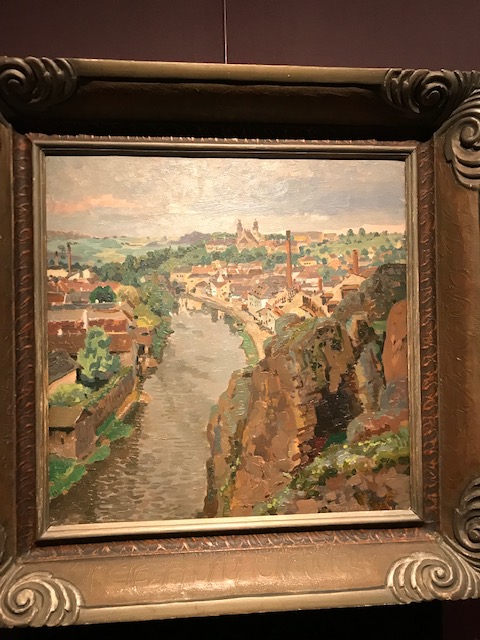

View of Třebíč, Bohumír Jaroněk
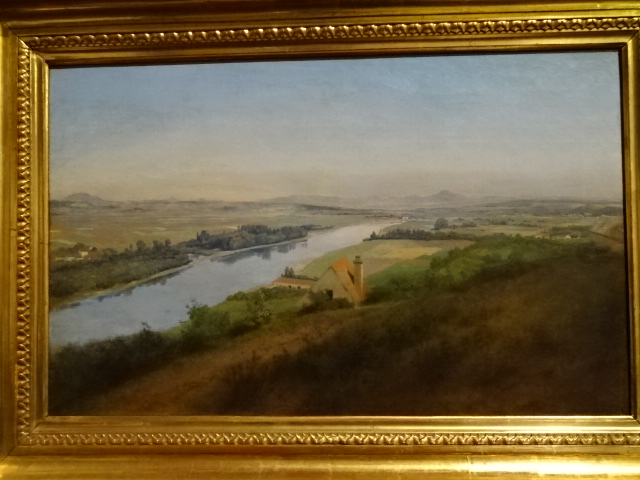
I loved the paintings of other towns, too, such as Jaroslav Šetelík’s “Tábor” from 1926 and his “Kutná Hora” from 1920. Bohumír Jaroněk’s “View of Třebíč” (1910) showed a river flowing through the center of the city, making the painting especially picturesque. Kutná Hora, Tábor and Třebíč are towns with fascinating history and intriguing sights. All three paintings brought to mind my trips to these towns and the sights with which I had become very familiar.
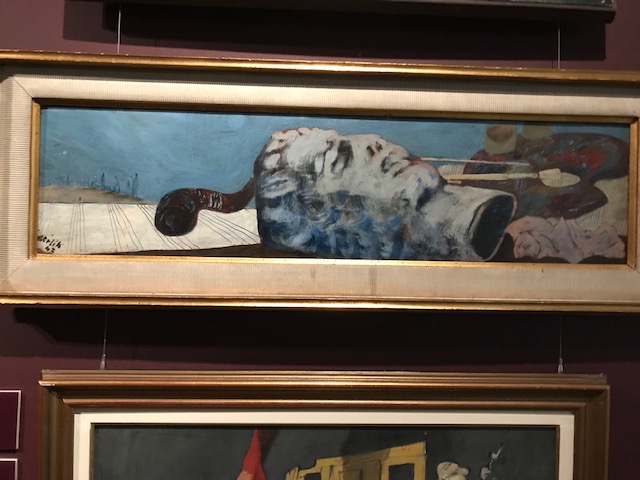

Painter’s Still Life, Arnošt Paderlík
Arnošt Paderlík’s “Painter’s Still Life” from 1943 takes on the theme of the suffering of mankind during wartime. This painter, sculptor, graphic artist and professor spent much of World War II making expressive, anti-military compositions ripe with hidden meanings. This particular painting shows, among other objects, an ancient bust from a statue. It has fallen on the ground, onto its side. After World War II, he drastically changed his style, devoting his time to still lifes that were inspired by Cubists Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque.
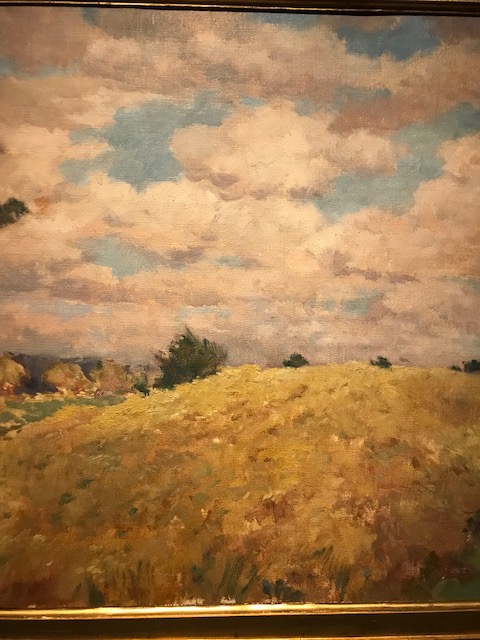

Rye, Antonín Slavíček
Paderlík delved into architectural adornment as well. His ceramic ornamentation graces the Kotva Department Store in Prague, and a bronze figure he designed is located at the Thermal Hotel in Karlovy Vary. I thought back to the sculptures and paintings I had seen throughout Europe, depicting the horrors of war. Even though he was focusing on World War II, Paderlík’s painting speaks to wartime oppression in general.
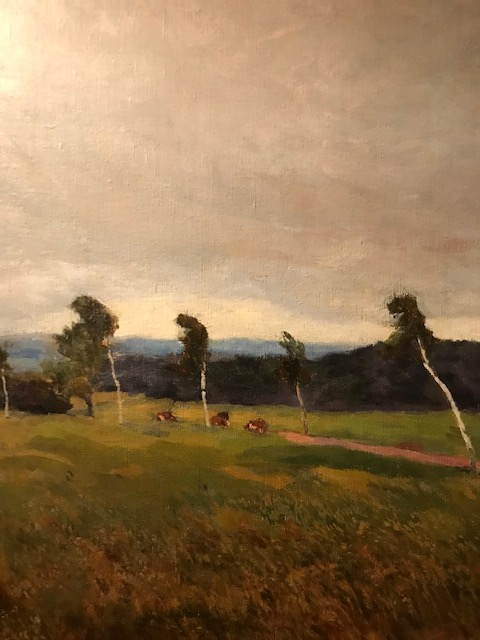
Landscape from Kameníčky, Antonín Slavíček
I was ecstatic that Antonín Slavíček’s landscapes, influenced by Impressionism, were represented in the exhibition. His “Landscape from Kameničky” from 1906 captured my undivided attention as did his “Rye” from 1908. He masterfully evoked the textures of the grass and dirt road in “Landscape from Kameničky.” I felt as though I could reach into the painting and touch the grass and dirt. I have always been drawn to the emotional quality of his works and to the strong use of color that permeates his renditions, including “Rye.” Slavíček was a student of Julius Mařák, perhaps the most prominent Czech landscape painter of the 19th century, who also worked as a professor promoting realism to many talented artists.
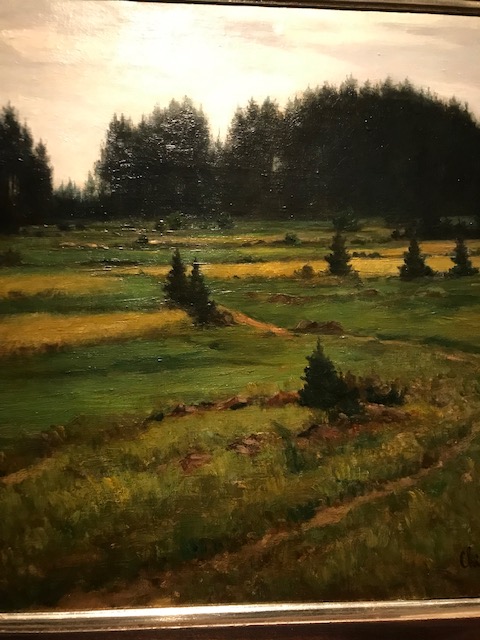

Meadow, Antonín Chittussi
The work of one of the most important Czech painters of the 19th century, Antonín Chittussi, also was highlighted in the exhibition. His nature-themed canvases evoked strong emotions in me. His painting “Meadow” from 1886 made me take a deep breath as all tension and stress in my life momentarily disappeared. I also was gripped by his realist portrayal of sheep and a shepherd in “On the Pasture” (1882).
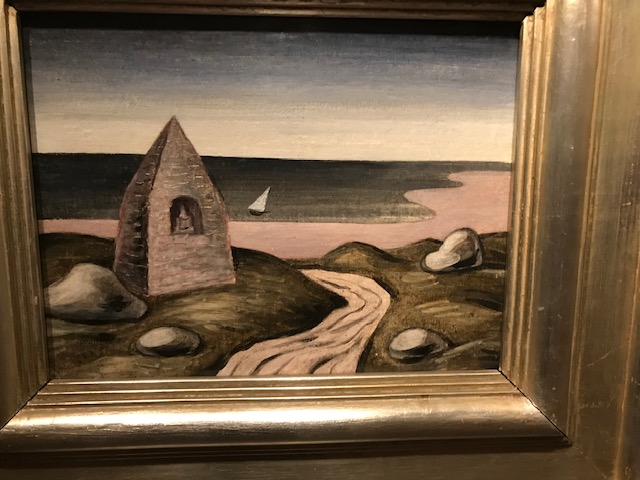
Chapel of Saint Brandan, Jan Zrzavý
Jan Zrzavý, one of my all-time favorites, was highly influenced by Italian primitive art and Symbolism. He also utilized light and color masterfully. His works have fantasy-like and mystical elements that correspond to magic realism. He didn’t only master painting but also graphic art, illustrations, teaching and scene design – all fields in which he worked for the National Theatre during the 20th century. Some of his paintings, such as his rendition of the “Chapel of Saint Brandan” (1946), evoke sadness and solitude, delving into the darkest depths of the human soul. I noticed the dominant greys in the painting, such as that of the gloomy winding lane. On the dark water floated a solitary sailboat.
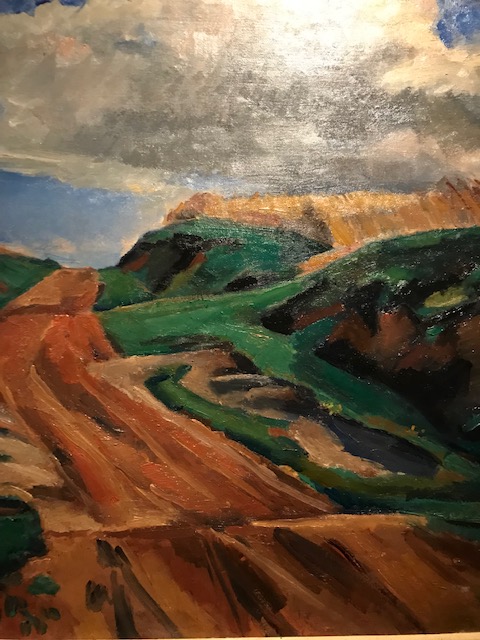

Summer Landscape, Václav Rabas
One of the first Czechs to receive recognition as a national artist, Václav Rabas studied under the guidance of Max Švabinský and fought on the front in World War I, where he was injured and subsequently sent home. Influenced by 19th century landscape painting and the art of Paul Cézanne, Rabas created canvases rich with color, and some of his works showed features of magic realism. I loved the vibrant colors in his Summer Landscape (1930). His landscapes concentrated mostly on his native Rakovník. Rabas was not only a landscape painter by any means. Indeed, he excelled at rendering the human figure with his 1923 cycle of “Czech Heads” that represented famous personalities. Rabas also created 24 paintings demonstrating how to make bread.
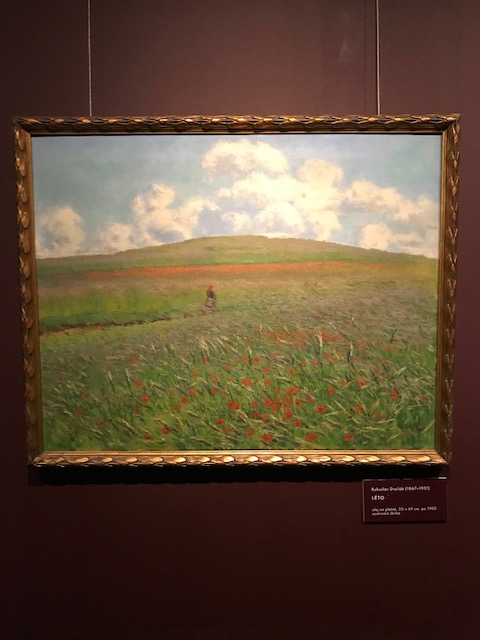

Summer, Bohuslav Dvořák
I felt like running through the meadow in Bohuslav Dvořák’s “Summer” (1902). I felt liberated, free to go my own way and follow my dreams while I peered at the painting. Dvořák studied under Mařák and began his career as a realist who was influenced by Chittussi. Later, though, he began to show more characteristics of Slavíček’s style. Color helped define his works, and some of his paintings had strong Impressionistic qualities.
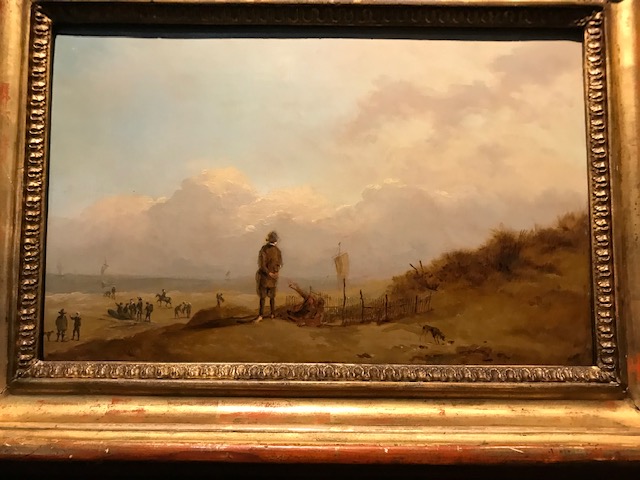

On the sea coast, Norbert Grund
I have loved the small landscapes by 18th century Norbert Grund for decades and was enthusiastic when one of his paintings was included in this exhibition. His “On the Sea Coast” (1750) shows a man with his back to the viewer as he gazes at the sea and beach, where other people were present. The versatile Rococo artist was known for genre paintings, landscapes and biblical works. Whenever I saw one of Grund’s creations, especially a landscape, I felt drawn into the world of the painting because the works entranced me so much.
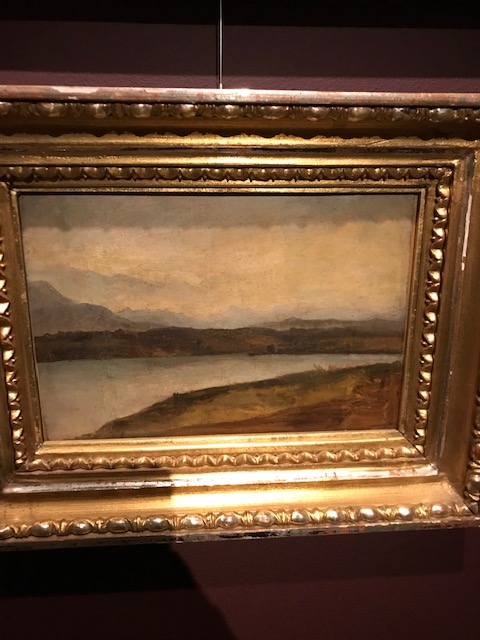

Motif from Gmundenu, Josef Mánes
Perhaps the most influential painter of the 19th century, Josef Mánes created “Motif from Gmundenu” in 1843. His landscape paintings and portraits fall into the styles of Romanticism and Realism. Hailing from a family of painters, Josef Mánes made around 500 works. Best known for painting the 1865 allegorical calendar on Prague’s Astronomical Clock, Josef Mánes also created portraits of Prague inhabitants and landscapes of the Moravian countryside.
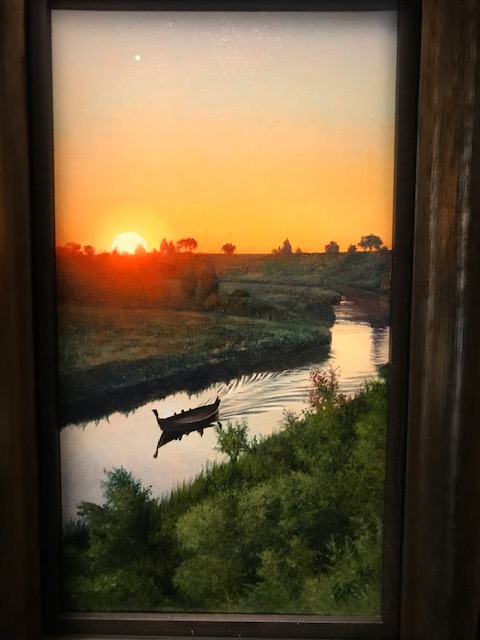

Sunrise – Horizon of Hope, Ivan Exner
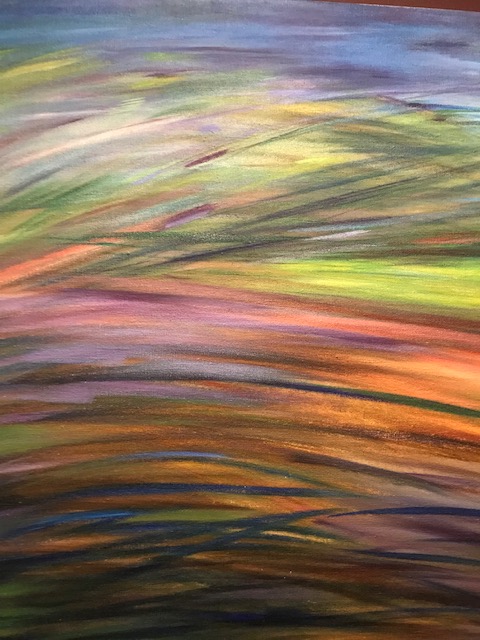
Landscape, Vojtěch Malaník
While some paintings hailed from the 18th and 19th centuries, others were contemporary and made just as strong an impression. Vojtěch Malaník’s “Landscape” from 2015 featured a mesh of lines of bright color, an abstract creation showing the vitality of nature in a very dynamic way. Ivan Exner’s “Sunrise – Horizon of Hope” (2024) was mesmerizing with its bright yellow sun rising in the pink and orange sky. An empty boat floated on the river as sunrays danced on the water.
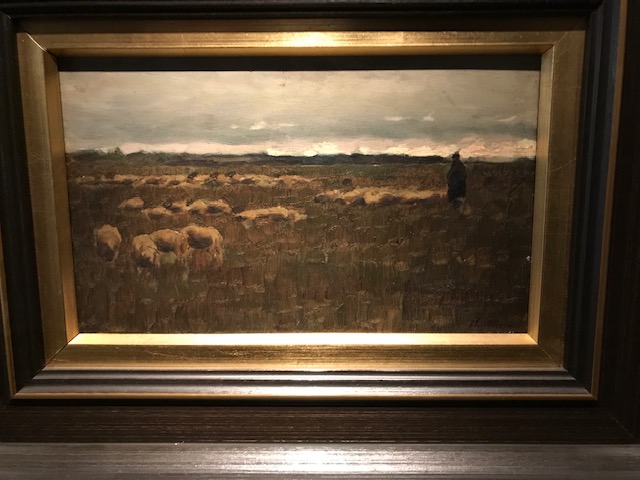

On the Pasture, Antonín Chittussi
These are just a few of the masterpieces on display in this exhibition. Every painting spoke to me, narrating vibrant stories through nature, mythology and war. Lyricism and romanticism as well as realism punctuated this art show. While some stories were gloomy and foreboding, others were joyful and bright. I saw nature as a powerful force that mankind could not control. I sensed times marked by hope as well as days denoted by darkness. This was a poetic and powerful exhibition focusing on the joys and tribulations of life.
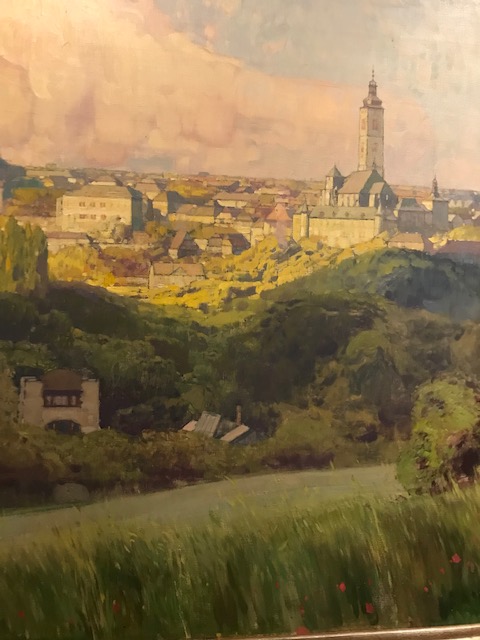

Kutná Hora, Jaroslav Šetelík
Tracy A. Burns is a writer, proofreader and editor in Prague.





































