The following is my own personal list of Czechs who, throughout the centuries, have contributed in a positive way to Czech culture, art, politics and other fields. There are many people I left out because I do not feel they played a positive role. Others I simply forgot and will have to add at a later date.
Tomáš Baťa (1876 – 1932)
Born April 3, 1876 in the southeastern Moravian town of Zlín, Tomáš Baťa became a leading entrepreneur in a family that has received accolades for its long and impressive history in shoemaking. The Bata clan began making shoes as early as 1667. Not only did he found shoe factories throughout the world, but he also was the Zlín’s major from 1923 to 1932. He was responsible for transforming Zlín into a modern city, building schools, for example. He was greatly improved the educational system, too. Even though Baťa died in a plane crash during 1932, the company Baťa Shoes remains successful to this day.
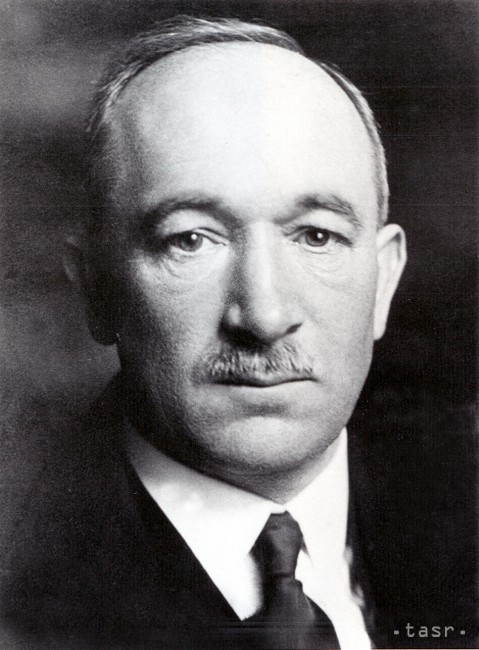

Edvard Beneš from TERAZ.sk
Edvard Beneš (1884 – 1948)
Beneš served as second president of Czechoslovakia from December of 1935 to October of 1938, when he resigned, convinced that the Munich Agreement was unfair. He became president of the Second Republic during June of 1946. Beneš asserted that the Sudeten Germans were collectively responsible for the destruction of independent Czechoslovakia, and he instigated the Beneš decrees, which involved confiscating the property of Germans, traitors and collaborators, taking away their Czechoslovak citizenship and expelling them from the country. Beneš also was the first Czechoslovak Minister of Foreign Affairs when Czechoslovakia was founded during 1918: He held the post of Prime Minister for a year and served as a Member of Parliament for a lengthy period. Beneš was very active in the fight for Czechoslovak independence during World War I and in the resistance movement during the Nazi Occupation.
Karel Havlíček Borovský (1821 – 1856)
Often referred to as the founder of Czech journalism, satire and literary criticism, Karel Havlíček Borovský was not only a journalist and critic. He also penned poems, was active in politics and worked as a publisher. His book Pictures from Russia presented the first Czech objective view of life in that country during that particular era. He established the first Czech daily newspaper, Národní noviny, known for its liberal viewpoints. Borovský was by no means a fan of the Habsburg Empire. He was tried several times for his sharp criticism of the monarchy. Borovský was expelled from the Czech lands and then lived in the Tyrol for almost four years. Though a pragmatist, he also supported universal suffrage. For a short time he served with the Austrian Empire’s Constituent Assembly but then opted to focus on journalism once again. He also translated works by Gogol and Voltaire into Czech. His book Tyrol Laments describes his arrest and subsequent expulsion to the Tyrol with humor and satire. He also is known for his poem “King Lavra,” a piece punctuated by allegory and satire.
Petr Brandl (1668 – 1735)
A leading Baroque painter in Bohemia, Petr Jan Brandl created emotional paintings using strong chiaroscuro. His works feature a powerful, passionate movement of colors, dramatic tension and a distinct tenderness. He authored more than 60 paintings and numerous drawings, all of which are scattered throughout Bohemia from Chyše to Hradec Králové, Prague to Litoměřice and Kutná Hora to Kuks, for instance. Prague’s National Gallery even has an entire hall filled with his paintings, including his famous “Simeon with the Baby Jesus.”

Vlasta Burian from ceskatelevize.cz

Vlasta Burian from revue.idnes.cz
Vlasta Burian (1891 – 1962)
Nicknamed “The King of Comedians,” Burian was a film and theatre actor, director, singer, writer and mime, for instance. During the First Czechoslovak Republic (1918 – 1939) his popularity soared. After the war he was wrongly accused of collaboration with the Nazis. He started out in cabarets and later established his own theatre, where he worked from 1925 until May of 1945, when it was nationalized. During 1944 the Germans closed his theatre for a while and after the war he was imprisoned twice. When he was freed, he found himself destitute. His villa in Hanspaulka and almost all his property and belongings had been taken away from him. He had to do manual labor working in the mines, for instance during a five-year ban when he was not allowed to act. He returned to acting, but the stints in prison had taken a toll on his health. He had to act even when he was ill for financial reasons. From 1923 to 1956 he made four silent films and 36 with sound. He was known for his improvisation, black humor and satire as well as his uncomplicated humor. He played roles of people in many professions. During 1994, he was rehabilitated. In 2002 his grave was moved from the cemetery in Prague’s Vinohrady to the famous Vyšehrad Cemetery, where Czech national figures rest.
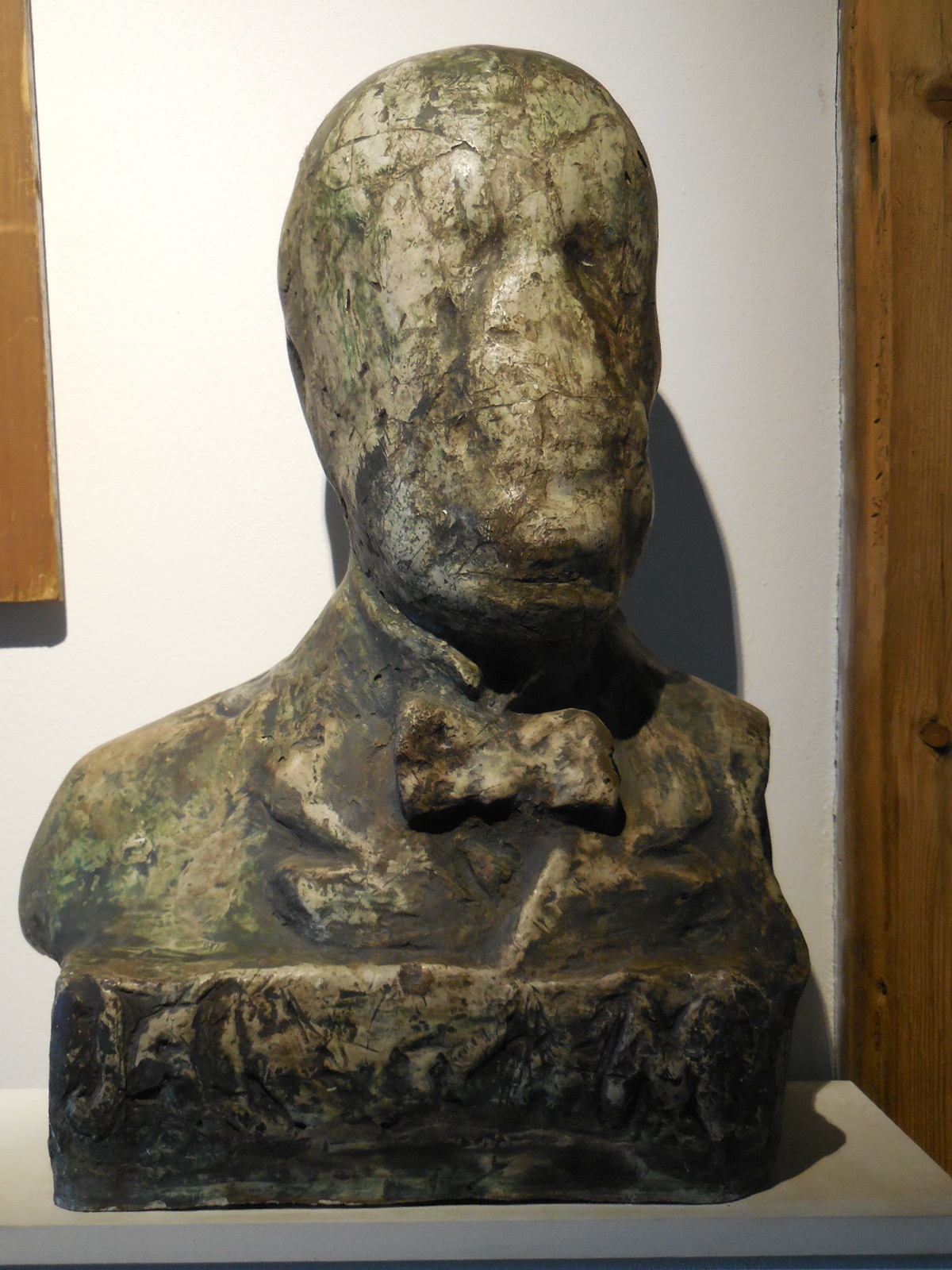

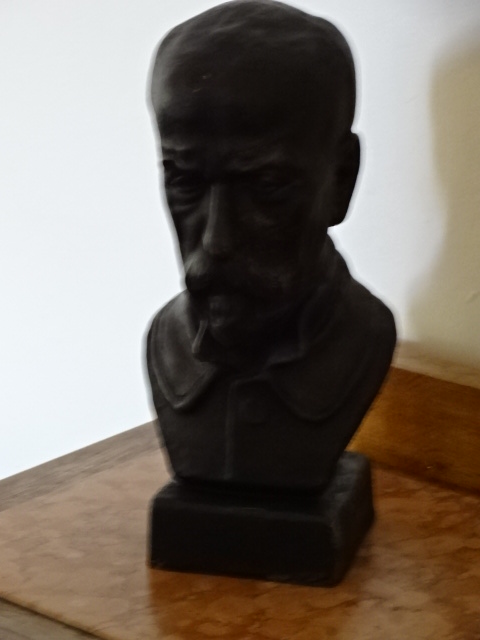
Bust of Jára Cimrman
Jára Cimrman (Born during a freezing February night between 1854 and 1872 – ?)
The 15 plays in the repertoire of the Jára Cimrman Theatre revolve around the fictional, unlucky outsider and genius Jára Cimrman, who lived in the Austrian part of the oppressive Austro-Hungarian Empire, during an era of Germanization when the Habsburgs were on the throne. Voted the Greatest Czech in a poll during 2005, Cimrman was a Czech nationalist who abhorred the Habsburg regime. Cimrman was a man of all trades – a seasoned traveler, prolific writer, collector of fairy tales, philosopher, filmmaker, gynecologist, dentist, teacher and criminologist, among others. While serving time for making fun of the emperor, he formed a choir and orchestra with his fellow prisoners and organized contests in Morse Code. His many inventions and accomplishments were only brought to light in 1966, when Zdeněk Svěrák (who co-authored the plays with Ladislav Smoljak) and his relative come upon Cimrman’s bust and papers at Liptákov 12, in a cottage in a village of the north Bohemian Jizera valley. His parents, an Austrian actress and a Czech tailor, forced him to wear girls’ clothing until he was 15 years old. The plays are laced with the typically Czech sense of humor that has allowed Czechs to survive a past riddled with oppression. All the plays take place around the turn of the 20th century, with the last one focusing on Cimrman’s life during World War I.

Josef Čapek from Muzeum bratří Čapků
Josef Čapek (1887 – 1945)
Karel Čapek’s older brother, Josef made a name for himself as a painter, writer, journalist, photographer, graphic artist and book illustrator. He authored books with his brother early in their careers, including the play From the Life of Insects. Josef also wrote books without his brother, such as a mystery and some art-related works. He was a Cubist painter who utilized simple, geometric shapes and severe lighting contrasts. He was very inspired by “primitive” art and often rendered members of the lower class in his creations. A supporter of democracy, Josef was arrested by the Gestapo on September 1, 1939 and then spent the next six years in concentration camps. He died shortly before the Germans lost the war. His symbolic grave is at Prague’s Vyšehrad Cemetery.

First President of Czechoslovakia Tomáš G. Masaryk with Karel Čapek
Karel Čapek (1890 – 1938)
The most versatile and perhaps most prominent writer in Czech history was a true Renaissance man –he was a playwright, novelist, feuilletonist, travel writer, story writer, journalist, children’s author, biographer, essayist, illustrator, photographer and translator. In the early years he often collaborated with his brother Josef, an accomplished artist in his own right. Karel Čapek argued that each person has his or her own truth, showed many perspectives of reality and criticized modern society. His writings also expose fears of Fascism, describe everyday events and warn against the abuse of technology. His works include Tales from One Pocket and Tales from the Other Pocket, War with the Newts, The Gardener’s Year, The Makropulos Thing, From the Life of Insects and R.U.R., a play which first used the word “robot.” He is buried in Prague’s Vyšehrad Cemetery.
Miloň Čepelka (born 1936)
A brilliant actor, Čepelka is best known for his roles in the plays of the Jára Cimrman Theatre, where he has graced the stage for half a century. The former teacher and reporter with Czech Radio dazzles the audience in plays such as Hospoda Na mýtince (The Glade Tavern), České nebe (Czech Heaven), Akt (The Nude) and Cimrman v říší hudby (Cimrman in the Paradise of Music), for instance. His singing in Cimrman v říší hudby is extraordinary. In Vražda v salonním coupé (Murder in the Parlor Car) he teams up with his son, who is also an actor. His biography Nedělňátko was published in 2016. He is also an accomplished poet and prose writer.
David Černý (born 1967)
A rebel artist, Černý never fails to spark controversy with his shocking and provocative creations set in public areas. He has painted a Soviet tank pink and designed male figures that urinate into an enclosure shaped like the Czech Republic, for instance. His 1997 creation “Hanging Man” consists of a 220-centimeter Sigmund Freud hanging by one hand onto a roof of a building on Prague’s Husova Street. In the main passage of Prague’s Lucerna Palace, his 1999 “Horse” shows Saint Wenceslas on an upside-down horse. Located in a courtyard in front of Prague’s Quadrio shopping center near Národní třída, his monumental installation of the head of Franz Kafka, also referred to as The Metamorphosis, consists of 42 moving layers that rotate 360 degrees and occasionally align to resemble Franz Kafka’s head. Weighing 39 tons, the Metamorphosis measures 11 meters or 36 feet in height.
Charles IV (Karel IV) (1316 – 1378)
The first King of Bohemia to become Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV was crowned in 1346 and made Prague his capital. During his rule the city played a prominent intellectual and cultural role in Europe. A major patron of Prague, he also had the Charles Bridge built, established the first university in Central Europe and founded the New Town in the capital city. He had Karlštejn Castle built to safeguard the crown jewels.

Jan Amos Comenius (Komenský in Czech) from Dobré knihy
Jan Amos Comenius (1592 – 1670)
This 17th century religious and educational reformer was fiercely Protestant, a member of the Unity of the Brethren denomination (also called Unitas Fratrum) and its last bishop. His work and life focus on his relationship to God, and he became a religious refugee on more than one occasion, living in Sweden, the Holy Roman Empire, England, the Netherlands and other countries. Jan Amos Comenius (Komenský in Czech) wrote innovative textbooks, encyclopedias, dictionaries and philosophical and theological studies. He even penned one of the most prominent works of Czech literature, the allegorical The Labyrinth of the World and Paradise of the Heart. Some of his reforms of the school system are still in use today. Comenius contributed greatly to universal education, and it is no wonder that he is considered a symbol of the Czech nation.
Ema Destinnová (1878 – 1930)
A Czech opera singer born in Prague, she started her career successfully in Berlin and later became a member of New York City’s Metropolitan Opera, where she performed in Smetana’s The Bartered Bride, Puccini’s La fanciulla del West and Wagner’s operas, for instance. Because she had connections with the Czech resistance, her Czech passport was revoked in 1914. Two years later, when returning to the Czech lands from the USA, the Austrians accused her of espionage and placed her under house arrest at her chateau in Bohemia. During 1918 she was back in the limelight, singing on Czech stages. Even the first president of Czechoslovakia, Tomáš G. Masaryk, visited her at the chateau she called home. She died at the age of 51 and is buried among great contributors to the Czech nation at Vyšehrad Cemetery in Prague. She also wrote poems, songs, novels and plays.
Josef Dobrovský (1753 – 1829)
This philologist, historian and Jesuit priest played a significant role during the Czech National Revival, although he did not write in Czech. Dobrovský, one of Europe’s first and foremost linguists, founded Slavic studies in the Czech lands. He was a key figure in establishing the Royal Czech Society of Sciences and Prague’s National Museum. His writings focus on Slavic studies, historiography and philology. He also contributed to the study of archeology and botany.
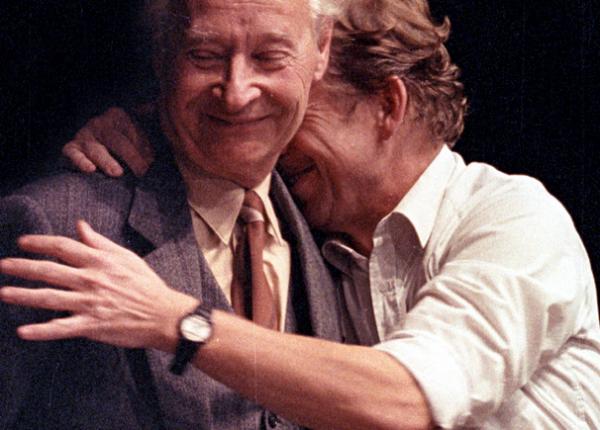

Václav Havel hugging Alexander Dubček, picture from Czech Free Press
Alexander Dubček (1921 – 1992)
Dubček is best known as the Slovak First Secretary of Czechoslovakia who instigated the liberal reforms of the Prague Spring in 1968, when the country experienced more freedoms. At that time, Czechoslovakia seemed destined to find its own individual identity while remaining a Communist country in what was called “socialism with a human face.” The Soviets put an end to the Prague Spring in August of 1968. Dubček also was a prominent politician before 1968 and after the Velvet Revolution of 1989. His life ended tragically on November 7, 1992.
Antonín Dvořák (1841 – 1904)
Neo-Romantic composer and head of Prague Conservatory, Dvořák was strongly influenced by Czech, Moravian and other Slavic folk music. The creator of nine symphonies, he is best known for From the New World, which was inspired by a tour of the United States. From 1892 to 1895, he worked as director of the National Conservatory of Music in New York City. His opera Rusalka has achieved worldwide acclaim. Dvořák also composed two sets of Slavonic dances, symphonic poems, songs, choral works, chamber music and piano music, for instance. He created the religious work Stabat Mater, the chamber piece Dumky Trio, the Cello Concerto and American String Quartet as well as the Moravian Duets. He admired Richard Wagner’s operas. The librettos of eight of his nine operas were written in Czech. He often travelled to England and also visited Russia.
Miloš Forman (born 1932)
This film director, screenwriter and professor greatly influenced the New Wave movement in the 1960s with movies such as Talent Competition, Black Peter, Loves of a Blonde and The Fireman’s Ball. During this time period he often focused on reality and everyday life, sometimes using individuals who had no acting experience to play main characters. After the Soviet tanks ended the Prague Spring of 1968, he emigrated to the USA, where he experienced more success. There, his films often dealt with themes of alienation and craziness. His 1975 hit One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest captured five Oscars, and his 1984 creation Amadeus nabbed eight Oscars. He also directed a film version of the musical Hair.

Josef Gočár (1880 – 1945)
One of the pioneers of modern Czech architecture, Gočár has created architectural masterpieces in Prague, Pardubice and Hradec Králové, to name a few places, implementing styles of Cubism, Rondocubism, Functionalism and Constructivism. His contributions to architecture between the two world wars have distinguished him as one of the most significant personalities in Czech architectural history. From the House of the Black Madonna in Prague to the development plan of modern Hradec Králové to the Grand Hotel in Pardubice, his awe-inspiring creations spectacularly dot the Czech landscape.
George of Poděbrady (1420 – 1471)
George (Jiří in Czech) of Poděbrady served as King of Bohemia from 1458 to 1471 and also was leader of the Ultraquist Hussites, who were not the radical branch of the Hussites. The Hussite wars in the 15th century set factions of Hussites against each other, and foreign armies took part, too. He was successful on the battlefield during these wars. He defeated the Austrian troops of King Albert II in one battle and greatly contributed to the demise of the extreme Taborite branch of Hussites in another battle. Though he made many efforts to get the confidence of Pope Pius II, the Pope did not approve of him. He often found himself in conflicts with Rome. Pope Paul II excommunicated George of Poděbrady when his nobles revolted against him.
Karel Gott (born 1939)
Often called the “Golden Voice of Prague” and the “Sinatra of the East,” singer and painter Karel Gott is a master performer of romantic ballads. Yet his success – from 1960 to the present – is largely due to a diverse repertoire that includes operas, classical compositions, jazz, musicals, rock ‘n roll, country, western and disco music. The most acclaimed singer in the country, he has performed all over the world.
Jan Grossman (1925 – 1993)
Grossman’s tenure as artistic director of Prague’s Divadlo Na zábradlí (The Theatre on the Balustrades) from 1961 to 1968 is considered one of the most significant eras of Czech postwar theatre. There, he directed Havel’s The Memorandum and The Garden Party, Jarry’s Ubu The King and Kafka’s The Trial, to name a few. He was punished by the Communists on numerous occasions. After the February 1948 Communist coup, he was expelled from university, forced to leave his job as lecturer at the National Theatre and banned from publishing for a lengthy period. When he again was allowed to work in the literary sphere, he edited books by significant Czech authors, including František Halas and Miroslav Holub. After the tanks of the Warsaw Pact countries entered Prague and the 1968 Prague Spring was crushed, he was no longer allowed to direct in Czechoslovakia. He had to work abroad. Then, in 1975, the Communists revoked his passport, and he was forced to do his directing in the country but outside of Prague. From 1989 to his death in 1993, he was once again creating stagings with Divadlo Na zábradlí, directing Havel’s Largo Desolato and Temptation as well as Moliere’s Don Juan and Bennett’s Kafka’s Dick.
Dominik Hašek (born 1965)
This legendary Czech goaltender was inducted into the Hockey Hall of Fame during November of 2014. His career spanned 16 seasons, as he represented the Chicago Blackhawks, Buffalo Sabres, Ottawa Senators and Detroit Red Wings. He also tended goal for Czech HC Pardubice and Spartak Moscow. Dubbed “The Dominator,” he starred in the NHL from the 1990s to early 2000s. From 1993 to 2001, he was awarded the NHL’s Vezina Trophy six times. He played a vital role on the Red Wings when they captured the Stanley Cup in 2002. Hašek holds the distinction of having the highest career save percentage ever in the NHL (0.9223). He was 43 years old when he retired.
Jaroslav Hašek (1883 – 1923)
This writer, journalist, pubgoer, hoaxer and anarchist is best known for his four-volume epic The Fortunes of the Good Soldier Švejk in the First World War, a picaresque novel focusing on the lovable idiot Josef Švejk, who messes up orders by acting them out literally. The book expresses the plight of the common man in the dawn of a new age and is famous for its Czech humor and anecdotes. Hašek also succeeded as a story writer – overall, he had about 1,500 stories in print. The writer fought in World War I but was captured and placed into a POW camp in Russia. Then he joined the Czech Legion. The former bank clerk and dog seller was no stranger to prison, as he was sometimes jailed for his unruly, bohemian behavior.
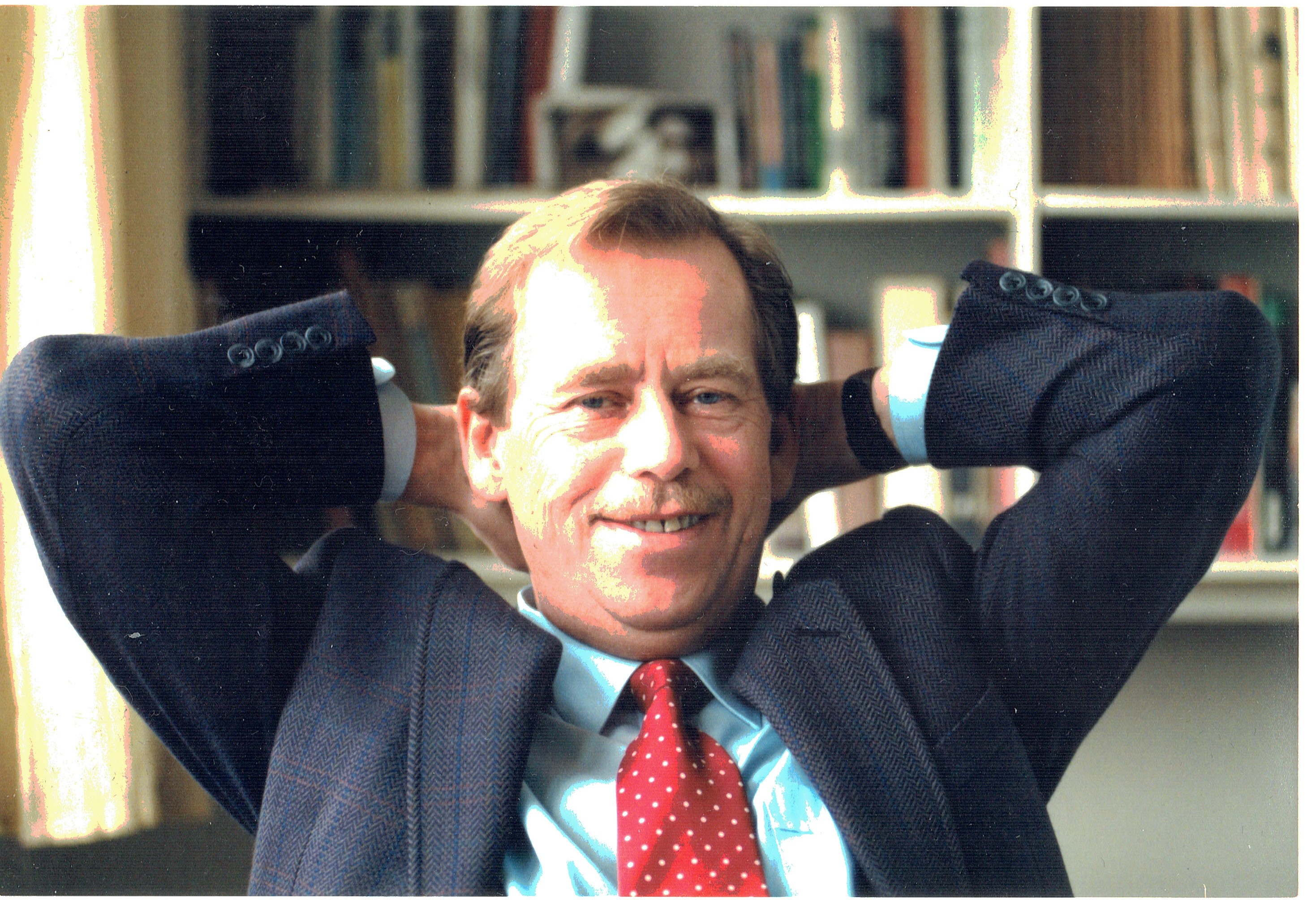

Václav Havel, former dissident and President of Czechoslovakia and the Czech Republic
Václav Havel (1936 – 2011)
The playwright-turned-president led Czechoslovakia and then the Czech Republic for a total of 13 years, shaping his nation into a Western style democracy. He was the first President of Czechoslovakia to be elected in a democratic election in 41 years. Under his guidance the Czech Republic became a member of NATO, and he contributed greatly to the Czech Republic’s acceptance into the European Union. He left the political sphere in 2003, During 2008, his play Leaving premiered in Prague and later was made into a film. Havel was one of the country’s most prominent writers, penning plays, essays, letters, poetry, memoirs and speeches. He worked as playwright and dramaturg at Prague’s Divadlo Na zábradlí during the 1960s, where his absurd plays such as The Memorandum, The Increased Difficulty of Concentration and The Garden Party were first staged. He helped instigate Charter 77, a document signed by dissidents, promoting human rights and taking a stance against the repressive regime. Havel was imprisoned for his dissident activities under Communism several times. He spent almost four years in prison from 1979 to 1983.
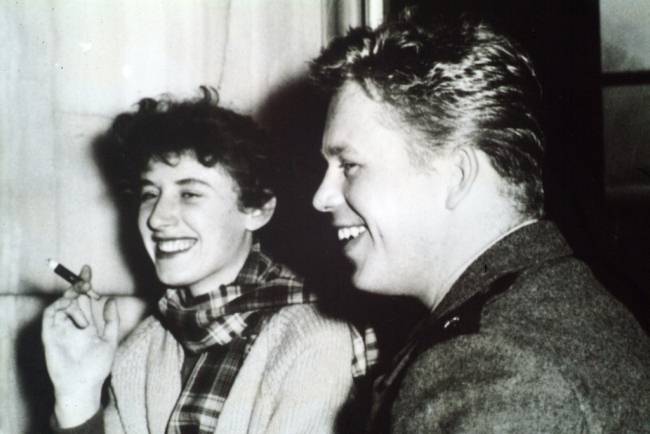

A young Olga Havlová and Václav Havel, photo from Knihovna Václava Havla
Olga Havlová (1933 – 1996)
The first wife of Czechoslovak and later Czech Republic President Václav Havel grew up in a working-class family with the name Šplíchalová, toiling in the gritty Žižkov district of Prague. This former First Lady worked in a factory after graduating from high school and later took on various jobs. She met Václav Havel for the first time in the first half of the 1950s and married him in 1964. A theatre and film enthusiast, Olga worked as an usher at The Theatre on the Balustrades during the 1960s, the same theatre where Václav served as dramaturg and staged his plays. She supported Václav’s dissident activities and even took part in them herself. From 1979 to 1983, Olga was the recipient of her husband’s letters from prison. Later, this correspondence would be published as the philosophical Letters to Olga. She co-founded the underground video magazine, Original Videojournal, which documented dissident activities. Olga also was a driving force behind the founding of About Theatre magazine. From 1989 to 1996, as First Lady, she devoted her time to charities and set up the Olga Havlová Foundation, which helps people with physical impairments and others who are the subject of discrimination in society. During 1991 a Norwegian Foundation named her Woman of the Year, and in 1995 Czechs awarded her that honor. In 1997, she posthumously received the Czech Republic’s Order of Tomáš G. Masaryk. A documentary film about her life nabbed the Czech Lion award for best documentary in 2014.
Milada Horáková (1901 – 1950)
A champion of women’s rights and democratic principles, Horáková was executed by the Communists on June 27, 1950. Her opinions and criticism of the regime had made her a target for the Secret Police, who incarcerated her on trumped up charges of conspiring to overthrow the republic. A show trial, reminiscent of those during the Great Purges of the 1930s in the Soviet Union and enforced by Soviet advisors, ensued. She received the death penalty. Horáková’s hanging marked the death of an anti-Nazi and anti-Communist fighter who had fervently fought for democracy and the ideals of first Czechoslovak President Tomáš G. Masaryk.
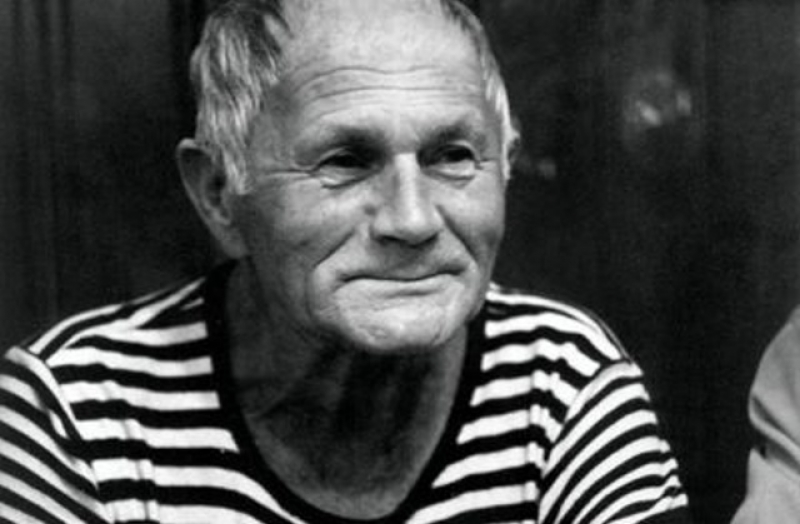

Bohumil Hrabal, photo from Moderní-Dějiny.cz
Bohumil Hrabal (1914 – 1997)
This life-long pubgoer had a literary career that spanned six decades. He is noted for his grotesque, absurd and irreverent humor and anecdotes and often wrote in Prague dialect. While he is best known for his fiction, he scribed impressive poetry during the early years. Hrabal created the pábitel character, a dreamer living on the outskirts of society who often speaks in meandering, whimsical anecdotes. Hrabal held a myriad of jobs – train dispatcher, trainee lawyer, insurance broker, traveling salesman, paper baler and theatre stagehand, to name a few. He also worked at the Poldi steelworks in Kladno. After the Soviet tanks rolled into Prague during August of 1968, the Communists banned Hrabal’s writings. On February 3, 1997 he either fell or jumped to his death from a fifth floor window of the hospital where he was receiving treatment. Hrabal’s works in English include Dancing Lessons for the Advanced in Age, Harlequin’s Millions, Too Loud A Solitude, I Served the King of England, In-House Weddings, Pirouettes on a Postage Stamp and Closely Watched Trains, which was made into a film by Czech director Jiří Menzel and received an Oscar.
Rudolf Hrušínský (1920 – 1994)
One of the greatest Czech actors of all-time, Hrušinský hailed from a family famous for its contributions to theatre and film. After sojourns with E. F. Burian’s avant-garde D 39 Theatre and Prague’s Municipal Theatre, he became a member of the National Theatre, where he graced the stage from 1960 to 1992. When, in 1968, he signed dissident Ludvík Vaculík’s 2,000 Words, protesting against the totalitarian regime, Hrušinský was severely punished by the Communists: He could no longer teach at the theatre university, act in film or television or take part in radio broadcasts. Later he was permitted to take up acting again. Some of his dazzling performances on stage took place in plays Ubu The King, Much Ado About Nothing, The Makropulos Thing and The White Plague. After the 1989 Velvet Revolution, he acted in Hrabal’s I Served The King of England along with one of his sons and his grandson at the Činoherní Klub. A prominent actor in films as well as in the theatre, he is known for his roles in the movies The Good Soldier Švejk, The Summer of Caprice, My Sweet Little Village, The End of Old Times, The Cremator, The Death of the Beautiful Deer and Larks on a String, to name a few.

Jan Hus, photo from MojblognaATLAS.SK
Jan Hus (1370 – 1415)
Hus was a religious reformer, priest, university lecturer, preacher and Czech nationalist symbol who influenced Martin Luther. Inspired by the writings of John Wycliffe, Hus played a major role in the development of Protestantism and emphasized the moral weaknesses of the clergy when speaking from the Bethlehem Chapel in Prague’s Old Town. The Pope and Archbishop were far from pleased with his ideas. In 1414, he was called to defend himself at the Trial of Constance but was arrested immediately. He was burned at the stake as a heretic on July 6, 1415, a day considered the precursor to the Hussite Wars and now commemorated as a Czech national holiday. The Czech Brethren Church consists of his followers even today. Hus also was a pioneer of the Czech language, inventing diacritics. He was a prolific writer as well.
Leoš Janáček (1854 – 1928)
This Czech composer, teacher, folklorist, musical theorist and publicist was greatly influenced by the music of Antonín Dvořák and Moravian folk songs. He also was enthralled with Russian culture. His opera Jenůfa was dedicated to his daughter, who died young. He also is known for the opera The Cunning Little Vixen, the Sinfonietta that is inspired by his beloved Brno and the rhapsody Taras Bulba. From 1881 to 1919, he served as director of the school that became known as the Brno Conservatory. His string quartet, The Kreutzer Sonata, also is a top-notch work. He befriended theatre critic, dramatist and translator Max Brod, who published Janáček’s biography.

Jaromír Jágr, photo from Týden.cz
Jaromír Jágr (born 1972)
One of the greatest ice hockey players of all-time, right wing Jaromír Jágr helped the Pittsburgh Penguins to Stanley Cups in 1991 and 1992 and guided the Czech National Team to gold in the Winter Olympics in Nagano during 1998. He has played for the Florida Panthers, New Jersey Devils, Pittsburgh Penguins, Washington Capitals, New York Rangers, Philadelphia Flyers, Dallas Stars and Boston Bruins, for instance. He also skated in Russia with Omsk of the Kontinental Hockey League during three seasons. He served as captain of the Pittsburgh Penguins and New York Rangers. Jágr has won numerous awards in the NHL, including the Art Ross Trophy as the league’s leading scorer numerous times.
John of Nepomuk (Saint) (1340/50 – 1393)
This martyr of the Catholic Church and national saint of Bohemia was tortured and drowned in Prague’s Vltava River. Historians argue about the reasons for his horrendous fate. One possibility involves his being condemned to death by Bohemian King Wenceslas IV when he refused to divulge the queen’s secret confessions to the king while John of Nepomuk was the queen’s confessor. Another version states that King Wenceslas IV and John of Nepomuk disagreed on the appointment of an archbishop. He is now considered to be the patron saint against catastrophes, floods and drowning.
Josef Jungmann (1773 – 1847)
This linguist, translator and prose writer, along with Josef Dobrovský, is considered to have laid the foundations for the modern Czech language,. His most valuable work was his five-volume Czech-German dictionary, which includes the basis of modern Czech vocabulary. Jungmann put to use archaic words and borrowed words from other Slavic languages, and they became a part of the modern Czech language. He also wrote novels and polemic works. Jungmann translated into Czech from German, French and English, making the works of Milton, Schiller and Goethe available to Czech speakers. Emperor Ferdinand gave him with a medal for his dictionary.

Franz Kafka, photo from kultura.zpravy.idnes.cz
Franz Kafka (1883 – 1924)
This German-Jewish writer born and brought up in Prague authored The Trial, The Metamorphosis, The Castle and In the Penal Colony, to name a few. He worked for many years as an insurance clerk. Kafka’s characters cannot communicate with others and find themselves consumed by anguish in absurd situations that they cannot control. Kafka wrote of guilt and despair and satired bureaucracy. Born next to the Old Town’s St. Nicholas Church, Kafka is buried in the New Jewish Cemetery in the Žižkov district.
Ivan Klima (born 1931)
This versatile writer of prose, plays, essays, feuilletons and children’s books spent three and a half years in the Terezín concentration camp along with his parents, persecuted for their Jewish origins. Somehow they all survived. After the war he joined the Communist Party but was expelled in 1967, reinstated in 1968 and expelled again in 1970. From 1970 he was a banned author, having to publish illegally in samizdat. Klíma has won numerous awards for his writing. Some of his books in English are Love and Garbage, My First Loves, My Golden Trades, Judge on Trial and his autobiography, My Crazy Century.
Frantisek Křižík (1847 – 1941)
This inventor and electrical engineering guru created the automatic arc lamp and built the first electric railway in the Austro-Hungarian Empire, as trains made their way from Tábor to Bechyně. Thanks to Křižík, the first electric street car line in Czech lands ran through the Letná fairgrounds at the Jubileum Exhibition in Prague during 1891. It was 800 meters long. He perfected the design of electric street cars and constructed power stations, too. His equipment was used in 130 power stations during his lifetime.
Milan Kundera (born 1929)
One of the world’s most well-known and most translated Czech authors, Kundera has published poems, plays, prose and essays. He has lived in France since 1975, and the Communists revoked his Czechoslovak citizenship in 1979. Under the totalitarian regime his books were banned. His most significant works include the novel The Unbearable Lightness of Being (1984), which was inspired by Nietzsche’s philosophy and his first novel, The Joke, which criticizes the totalitarian regime. His writings have been inspired not only by Nietzsche but also by Rabelais, Robert Musil and Miguel de Cervantes, among others. Kundera used to write in Czech but since 1993 has penned his prose in French. He has been nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature several times.
Ivan Lendl (born 1960)
Born in Ostrava to two successful tennis players, Lendl continued the family tradition with a flourish, becoming the number one ranked player. He played a significant role in pro tennis during the 1980s and early 1990s and is considered to be one of the best players of all-time. He has won eight Grand Slam singles titles while competing in 19 Grand Slam singles finals and nabbed 22 Championship Series titles. Overall, he notched 94 singles titles. Lendl moved to the USA in 1981 and became a US citizen during 1992. Lendl retired in 1994, when he was 34 years old. An avid fan of Alphonse Mucha, Lendl owns an almost complete collection of this artist’s posters. An exhibition of his collection took place at Prague’s Municipal House during 2013.
Princess Libuše (pre-9th c.)
She is often called the “Mother of Bohemia.” According to legend, clairvoyant Libuše stood on a cliff on Vyšehrad Hill overlooking the Vltava River during the eighth century and predicted that Prague would be founded there. She and ploughman Přemysl Oráč established the Přemyslid dynasty, which lasted from the 10th century to 1306.

Bohumil Hrabal and Arnošt Lustig in U Zlatého tygra pub in Prague
Arnošt Lustig (1926 – 2011)
This prolific Czech Jewish author focused on the Holocaust in his novels, short stories, plays and screenplays. Lustig spent time in three concentration camps during World War II. In 1945 he made a daring escape and hid in Prague for the rest of the war. When peace arrived, he became a member of the Communist Party, but Lustig gave up his membership in 1967. He was forced to leave the country after the Soviet tanks crushed the Prague Spring of liberal reforms in 1968. Lustig settled in the USA, and in the early seventies began teaching at The American University in Washington, D.C. After he retired from the university in 2003, Lustig moved back to Prague. Many of his novels are available in English: A Prayer for Katerina Horovitzova, Dita Saxova, Night and Hope, Darkness Casts No Shadow, Lovely Green Eyes, Indecent Dreams and others. Many of his novels have been adapted for the big screen. In 2008 Lustig was nominated for the Pulitzer Prize.
Karel Hynek Macha (1810 – 1836)
This pioneer of Czech Romanticism died at the age of 25. Still, in such a short time, he found modern Czech poetry and wrote poetry. He authored one of the best poems in Czech literature, May (Máj), a lyric epic poem about a prisoner awaiting execution. It contains motifs of love, nature and country. Yet his writings did not receive much acclaim during his lifetime, and May was his only book that was published when he was alive.
Bohuslav Martinů (1890 – 1959)
This Czech composer created almost 400 works, including six symphonies, 15 operas, 14 ballet scores as well as orchestral, chamber and choral music, for instance. He is best known for his neoclassical style. The piano plays a major roles in many of his orchestral pieces. He also utilized Bohemian and Moravian folk melodies. Martinů lived in Paris from 1923 – 40 and then emigrated to the USA, settling in New York City. He wanted to go back to Czechoslovakia in the 1940s, but his hopes were dashed when Foreign Minister Jan Masaryk was murdered by the Communists in 1948. From 1953 to 1959, he resided in Europe. His compositions include Memorial to Lidice (1942), written for the village razed by the Nazis in Czechoslovakia. He also wrote the opera Julietta and the Double Concerto for Two String Orchestras.
Jan Masaryk (1886 – 1948)
The son of first Czechoslovak president Tomáš G. Masaryk, Jan made a name for himself as a Czech diplomat and politician. He worked as chargé d’affaires to the USA from 1919 to 1922 during the First Republic. From 1925 to 1938, he served as his country’s ambassador to Britain, but he resigned when the Nazis took control of the Sudetenland, which had been the part of Czechoslovakia with a German majority. He remained in London, acting as the Foreign Minister for the Czechoslovak government-in-exile during World War II. He continued to hold the same post after the war even though the Communist Party was becoming more and more powerful. Jan was still serving in this capacity after the February of 1948 Communist coup. On the morning of March 10, 1948, his body was discovered in the courtyard of Prague’s Černín Palace, where the Foreign Ministry has its offices. His corpse was found below his bathroom window. At first it was declared a suicide, but investigations in the 1990s and 2003 labelled his death as murder.
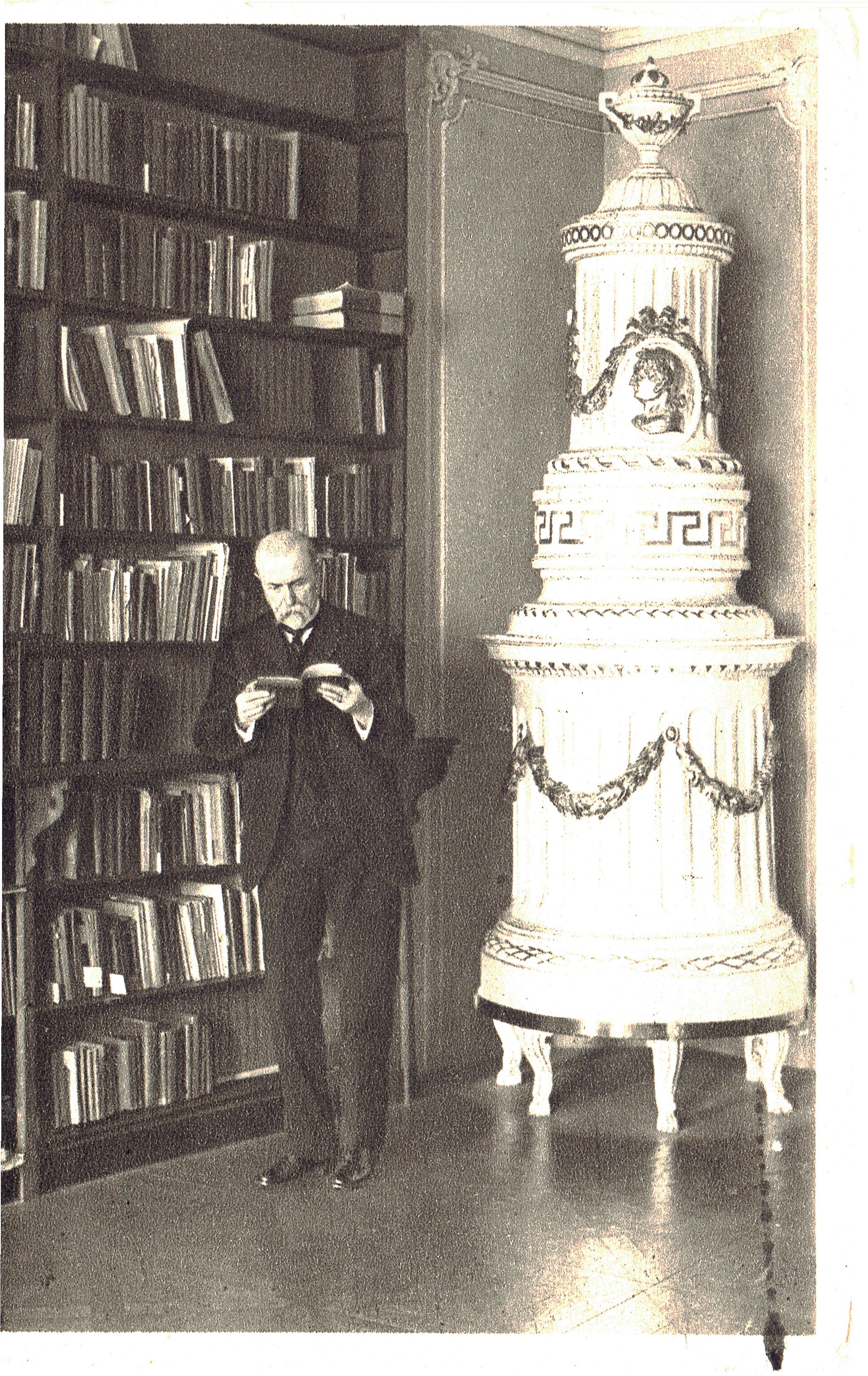

Tomáš G. Masaryk, first President of Czechoslovakia
Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk (1850 – 1937)
This philosopher, professor and prolific author held the post of Czechoslovakia’s first president for three terms that lasted 17 years. Guiding the government in exile during World War I, he argued for independence rather than autonomy. When he married the American Charlotte Garrigue, he adopted her last name as his middle name. Masaryk took a stance against antisemitism in the Hilsner Affair. He believed in giving minorities the right to embrace their national identities, freedom of the press and universal suffrage. He was convinced that a small nation could play a significant role in Europe. He also promoted the most contemporary advancements in science, the humanities and world literature. He viewed religion as a source of morality. Masaryk traveled to Washington, D.C., where he received the support of President Woodrow Wilson at the end of World War I for a sovereign republic of Czechs and Slovaks. This nation was founded as Czechoslovakia on October 28, 1918. He resigned for health reasons in 1935 and died less than two years later. In his writings he described the oppressiveness of tsarist Russia, analyzed causes of suicide and warned Czechs against the dangers of radicalism and escapism. He also criticized Marxism and supported the women’s movement. He was nominated for the Nobel Peace Prize 17 times.
The Mašín Gang – Ctirad (1930- 2011) and Josef Mašín (born 1932), Milan Paumer (1931 – 2010), Zbyněk Janata (1932 – 1955) and Václav Šveda (1921 – 1955)
The five anti-Communist fighters making up the “Mašín Gang” are remembered for their acts of sabotage in the early 1950s as well as for their 1953 death-defying escape to the West that covered 200 miles in 28 days. The group consisted of brothers Ctirad and Josef Mašín, Milan Paumer, Zbyněk Janata and Václav Šveda. During two raids on police stations to obtain weapons, the group killed two police officers. Then they shot a wages clerk to obtain 846,000 Czechoslovak crowns. During their escape, they were responsible for the death of three East German police officers. Their actions have triggered heated debates about whether they are heroes or villains.
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822 – 1884)
The father of genetics and the laws of heredity often referred to as Mendel’s Laws was a German-speaking Moravian scientist, born in Heinzendorf (now Hynčice, Czech Republic). Mendel was educated at an Augustinian monastery in Brno, where he also performed his experiments with plants. He founded the rules of heredity by examining seven characteristics of pea plants.
Jiří Menzel (born 1938)
This world-renowned director’s career in film was launched with his rendition of Bohumil Hrabal’s Closely Watched Trains, which won the 1966 Oscar for Best Foreign Film. My Sweet Little Village was nominated for an Oscar in 1985. Another much acclaimed film was Larks on a String, based on fiction by Hrabal. Other notable films he directed include the Summer of Caprice, The Beggar’s Opera, I Served the King of England and The End of Old Times. Since the 1970s he has devoted time to directing in the theatre as well, at home and abroad. He also has acted in films, appearing in Closely Watched Trains, The Cremator and Summer of Caprice, for instance.

Alphonse Mucha, from the web page of Jarmila Mucha Plocková
Alphonse Mucha (1860 – 1939)
The imaginative and passionate creations by legendary Art Nouveau painter and decorative artist Alphonse Mucha are well-known throughout the world, especially the idealized images of Sarah Bernhardt with her poignant, exhilarating gaze. An avid supporter of democratic Czechoslovakia, Mucha is also celebrated for his patriotic and folk art themes that celebrate not only the Czechoslovak nation but also Slav unity. He was prolific, creating posters, books, magazine and book illustrations, stained glass windows, jewelry, theatre sets, costumes and more. The Mucha style features beautiful, young women exuding optimism and happiness in extravagant, flowing robes designed in pale pastels. Flowers or crescent moons make halos around the enchanting figure’s head. He employed folk elements that were not only Czech but also Byzantine, Celtic, Rococo, Gothic and Judaic, among others. Tourists will not want to miss the opportunity to visit Prague’s Mucha Museum.
Martina Navratilová (born 1956)
Considered one of the best female tennis players of all-time, Martina Navratilová has an impressive list of accomplishments. She nabbed 20 Wimbledon titles and 18 Grand Slam titles. She remains the only player to ever rank first in both singles and doubles for over 200 weeks. She was the number one female in singles from 1982 to 1986. When she was given temporary residence in the USA during 1978, when the Communist government of her homeland revoked her Czechoslovak citizenship. She became a US citizen during 1981. She also has achieved much success as a tennis coach and has written several books.
Božena Němcová (1820 – 1862)
A significant writer during the Czech National Revival movement, she authored The Grandmother, based on memories of a happy childhood in the countryside. The main character, a grandmother, is a symbol of good, love and morality. The book has an optimistic tone. Němcová also wrote travelogues, fairy tales, legends and several other novels. The Grandmother has been made into a film and has been adapted for the stage.
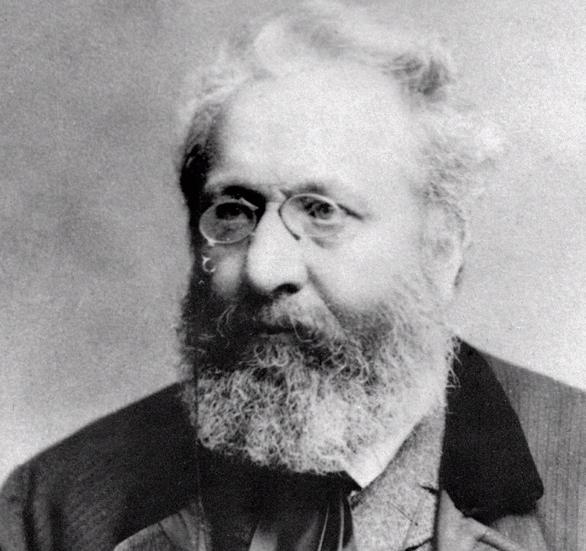

Jan Neruda, photo from ceskatelevize.cz
Jan Neruda (1834 – 1891)
This prolific writer of the Czech Realism movement was a poet, prose writer, journalist, playwright, literary critic, drama critic and translator. He hailed from Prague’s Little Quarter, and his collection of short stories, Tales of the Lesser Quarter (1877) are imbued with the special and magical atmosphere of this district. As a journalist he concentrated mostly on writing feuilletons and contributed greatly to the development of that genre. He wrote about everyday occurrences as well as exceptional events in Prague and its society. His prose also often was set in Prague. As a poet, though, he was pessimistic and skeptical. He also translated poetry, legends and national songs, for instance. He is buried in Prague’s Vyšehrad Cemetery, and the main street in the Little Quarter is named after him.
Jan Opletal (1915 – 1939)
This Charles University student was shot by German soldiers during the October 28, 1939 demonstrations against the Occupation. The strong believer in democracy died in the hospital November 11, 1939. His public funeral in Prague, held on November 15, became a spontaneous demonstration and would be the last big demonstration against the Nazis in the Protectorate. As a result, on November 17, German soldiers beat and arrested many students, even executing some and sending others to a concentration camp. Furious because of the demonstration at Opletal’s funeral, Hitler closed all Czech universities and dormitories for three years. Now November 17 is considered to be International Students’ Day and is a holiday in the Czech Republic.

Jan Palach, photo from vsezlate.blog.cz
Jan Palach (1948 – 1969)
The 20-year old Charles University student set fire to himself on Wenceslas Square in Prague on January 16, 1969, protesting the lack of freedoms and passivity of Czech citizens. He died in the hospital from his injuries. Palach’s funeral at Prague’s Olšany Cemetery on January 25 turned into a huge demonstration against the Soviet Occupation. After Palach’s death, the Communists imposed the rigid rules of the normalization era. Commemorating the 20th anniversary of Palach’s sacrifice, Jan Palach Week in 1989 was marked by many demonstrations against the totalitarian regime, and police used brutality in response to the protests. Dissident Václav Havel was arrested and imprisoned during Jan Palach Week in 1989.
František Palacký (1798 – 1876)
This Czech historian, writer and politician who greatly influenced the Czech National Revival movement is often called “The Father of the Nation.” His mammoth literary accomplishment, The History of the Czech Nation in Bohemia and Moravia is one of the most significant books in Czech history and remains an authority to this day. He traveled to archives all over Europe to do research on the work. Palacký, a nationalist and a Protestant, envisioned Czech history as a constant battle between Slavs and Germans. He was also very active politically. During the Revolution of 1848 he took an anti-German stance. In the 1860s he joined the Austrian senate as head of a nationalist-federal party called the Old Czechs. He promoted the idea of Czech autonomy with Bohemia, Moravia and Silesia belonging to a Czech kingdom.
Jan Patočka (1907 – 1977)
One of the most significant philosophers in Central Europe during the 20th century, Patočka dealt with the philosophy of educational reformer Jan Amos Comenius and the first president of Czechoslovakia, Tomáš G. Masaryk, among others. He also focused on the philosophy of history and contributed to Czech culture. Patočka came up with a unique philosophy of three movements in human existence – receiving, reproduction and transcendence. He was banned from teaching during the Nazi Occupation and also for many years by the totalitarian regime. His philosophical thought greatly influenced the dissident movement in Czechoslovakia from the 1960s through the 1980s. Patočka was one of the first signatories of Charter 77, a human rights movement in the country drafted in 1977. The Secret Police repeatedly interrogated him, and these lengthy interrogations triggered his death. At his funeral, Czechs demonstrated against the Communist regime.
Přemysl Otakar II (1233 – 1278)
Dubbed “The Iron and Golden King,” Přemysl Otakar II brought prosperity and prestige to the Czech lands as the fifth Czech leader, reigning from 1253 to 1278. With the exception of Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV, this energetic and well-educated ruler is the most revered Czech sovereign due to his penchant for promoting trade as well as making legal and other reforms. He created about 50 towns in Bohemia, Moravia, Silesia, Austria and Styria and founded Prague’s Little Quarter (Malá strana). He also had many castles built.
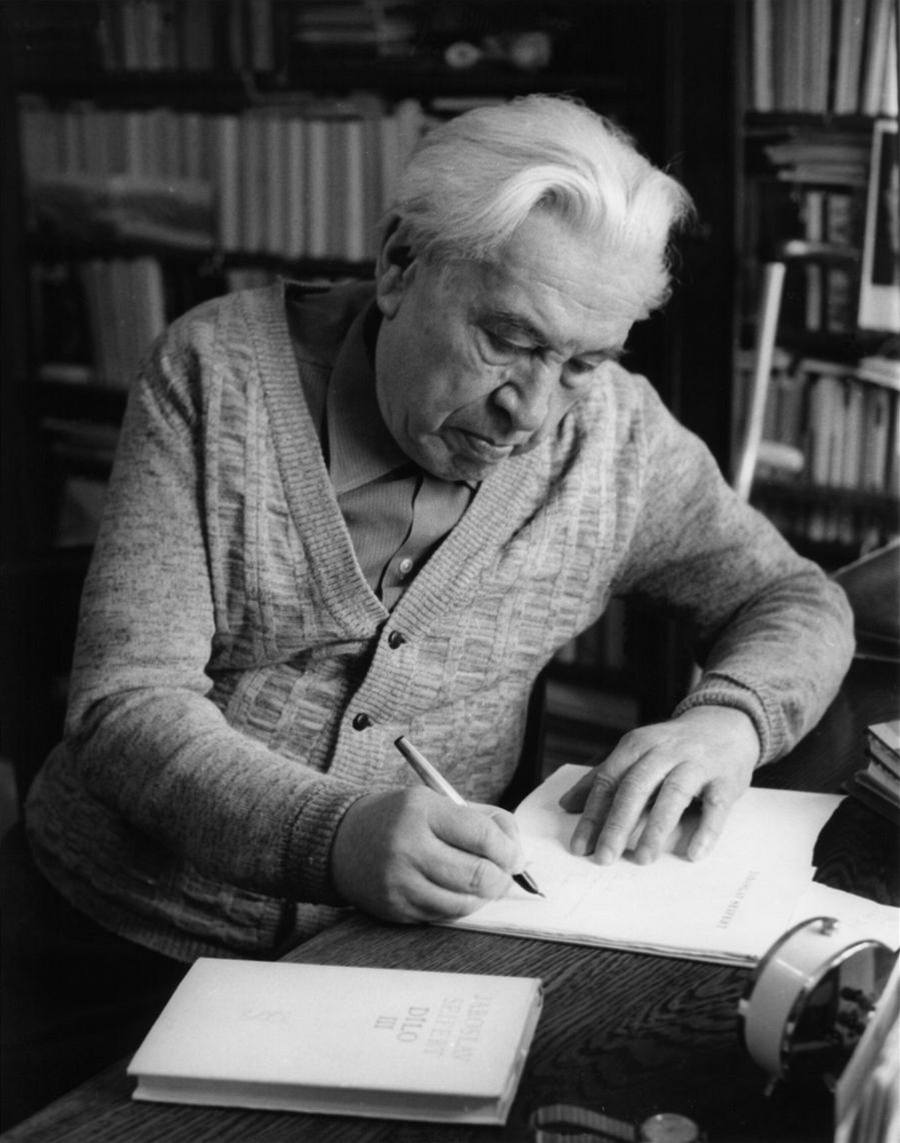

Jaroslav Seifert, photo from Web-Blog.cz
Jaroslav Seifert (1901 – 1986)
The only Czech to be awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature, Seifert was not only a poet, though he is best known for his works in this genre. He also worked as a journalist and translator, for instance. He published over 30 collections of poems. Seifert’s first poems appeared in 1921, and during the 1920s he was one of the founders of the influential journal Devětsil. Seifert signed Charter 77, a document calling for human rights and opposing the Communist regime. Even though his relationship with the Communist regime was complex, he was given the title of National Artist and received state prizes.
Bedřich Smetana (1824 – 1884)
An avid supporter of Czech nationalist identity, Smetana invented an entirely new genre of Czech opera. He composed eight operas, including The Bartered Bride and Libuše. He focused on Czech legends in his six symphonic poems called Má Vlast, and the Vltava movement in the symphony is always performed on the opening night of the annual Prague Spring Music Festival. A museum in Prague honors the composer who strove to express characteristics of the Czech people in his music.
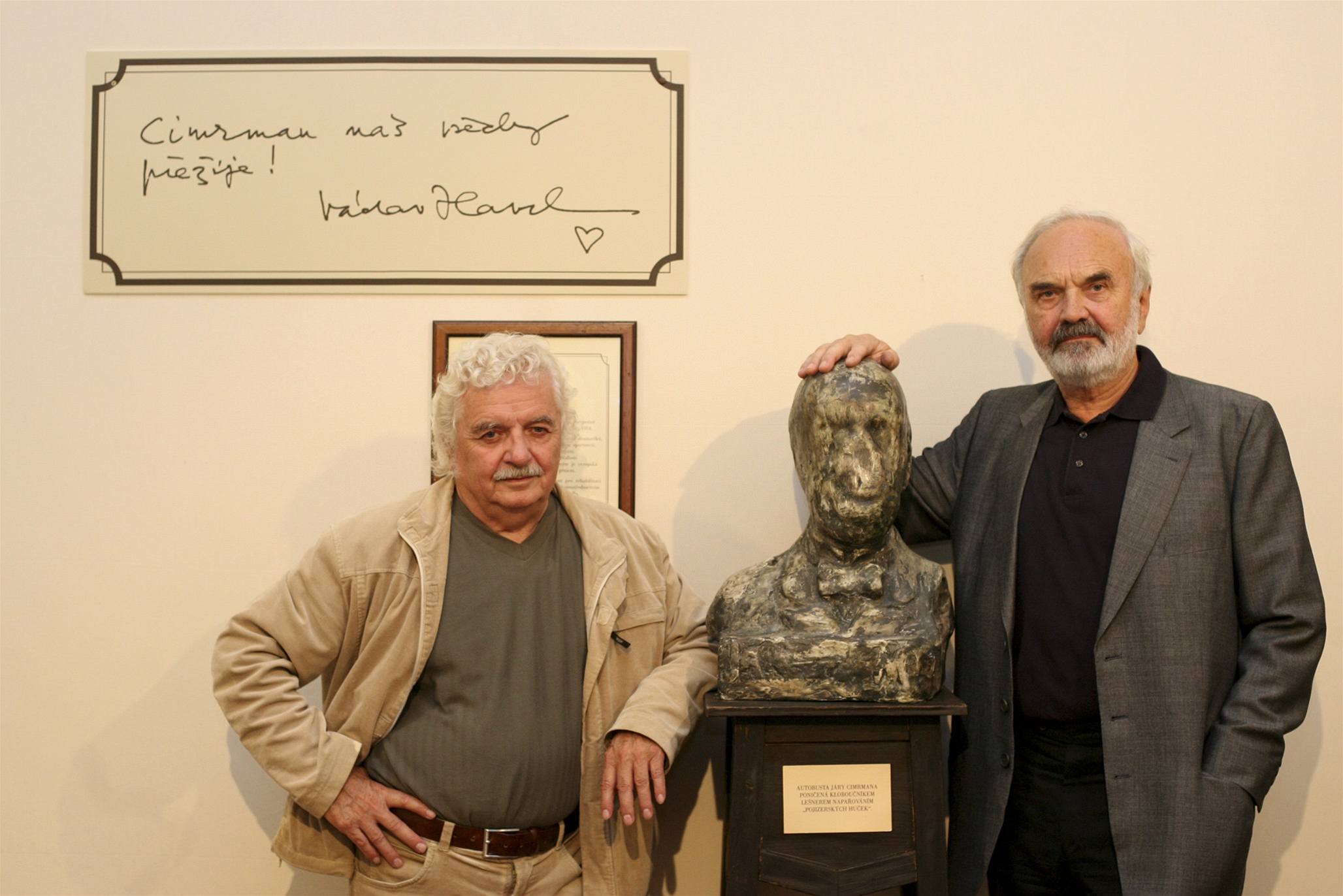

Ladislav Smoljak, the bust of Jára Cimrman and Zdeněk Svěrák, photo from lidovky.cz
Ladislav Smoljak (1931 – 2010)
Although he majored in mathematics and physics, Smoljak made a name for himself in the world of theatre and film. One of the three founders of the Jára Cimrman Theatre, he co-wrote for this theatre 13 plays with Zdeněk Svěrák and authored one by himself. He took on acting and directing in the ensemble. He was also a screenwriter and film director, often co-writing scripts with Svěrák. Smoljak was an expert on Czech comedy. A strong supporter of the Velvet Revolution, he was politically active as well. This dazzling performer for the Jára Cimrman Theatre was also an educator.
Josef Sudek (1896 – 1976)
Although he lost one arm while fighting for the Austro-Hungarian army during World War I, Sudek became one of the most renowned avant-garde photographers in the world and one of the most significant Czech photographers to work between the two world wars. A bookbinder by trade, he is best known for his photographs of Prague, including pictures of the interior of St. Vitus’ Cathedral and many photographs of the city at night. He also took snapshots of the interior of his studio and the views from its windows. Still lifes, landscapes and advertisements also make up the repertoire of his innovative work. While he focused on the Pictorialist style during the 1920s, most of his creations are considered to be in the Neo-Romantic style.
Josef Suk (1929 – 2011)
The grandson of composer Josef Suk and great-grandson of Antonin Dvořák, this violinist also played the viola and conducted. In 1961, he became a soloist for the Czech Philharmonic and performed with top-notch orchestras around the world. He gave concerts in the USA, Germany, Romania, France, Belgium and the Netherlands, for instance. He was renowned for his performances of pieces by Bach, Mozart and Beethoven. His rendition of Dvořák’s Violin Concerto received much acclaim. He also was a chamber musician, playing with the Prague Quartet, Suk Trio and Smetana Quartet. From 1974 to 2000, he conducted with the Suk Chamber Orchestra that he founded. Suk won many awards, including the National Order of the Legion of Honor in 2002.

Ladislav Smoljak and Zdeněk Svěrák in the play Afrika, photo from showbiz.cz
Jan Svěrák (born 1965)
The son of actor and screenwriter Zdeněk Svěrák has made a name for himself as one of the best filmmakers of his generation. His film Elementary School, which takes place shortly after the end of World War II, was nominated for an Oscar in 1991. His film Kolya nabbed an Oscar in 1996. He often teams up with his father in his work. Zdeněk Svěrák wrote the screenplays for Jan’s feature films Empties, Dark Blue World and The Three Brothers. His father acted in Elementary School, Kolya, Empties and The Three Brothers, too. Jan also filmed the documentary Papa, which focuses on his father’s intriguing life. Kuky Returns also received acclaim. During 2016 and 2017, he directed Barefoot Across the Stubblefield, a film based on his father’s biographical novella about life in a village during and after the Nazi Occupation. Jan also has received three Czech Lion Awards, a Crystal Globe and the Tokyo Grand Prix prize.
Zdeněk Svěrák (born 1936)
One of the most popular personalities in Czech culture, Zdeněk Svěrák is a man of many talents: He is an actor, screenwriter and writer of children’s books, stories and musical texts. Along with actor Ladislav Smoljak, he invented the fictional character Jára Cimrman, an unlucky Czech genius who, in his lifetime, did not get the credit he deserved for his masterful inventions and other achievements. Cimrman had been an inventor, detective, poet, writer of fairy tales, philosopher, gynecologist, dentist, philosopher and composer, for instance. Though fictional, Jára Cimrman was chosen the Greatest Czech in 2005. The extremely popular Jára Cimrman Theatre performs 15 of Cimrman’s plays set during the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Svěrák co-wrote 13 of the the plays, penned one by himself and acts in them. But Svěrák does not limit his acting to the stage. He is a well-known film actor and screenwriter, too. He has authored scripts that his son Jan has directed, including Kolya, which won an Oscar during 1996, Elementary School, also nominated for an Oscar, Empties, The Three Brothers and Dark Blue World. He also wrote and acted in the comedy Run, Waiter, Run! Other films in which Svěrák has cast his magical acting spell include My Sweet Little Village, The Snowdrop Festival, Larks on a String, Dissolved and Effused and Seclusion Near A Forest. His books in Czech include Stories, New Stories, Barefoot Across A Stubble Field and The Three Brothers.
Emil von Škoda (1839 – 1900)
Thanks to this prominent and industrious Czech entrepreneur, Škoda Works (now Škoda Transportation) became the largest industrial business in the Austro-Hungarian Empire and later in Czechoslovakia. At first the enterprise focused on steel but also manufactured equipment for sugar refineries, malt houses and breweries. Later, it became one of the largest manufacturers of weapons in Europe. Now called Škoda Transportation, the company concentrates on making trams, electric locomotives and rapid transit train systems.
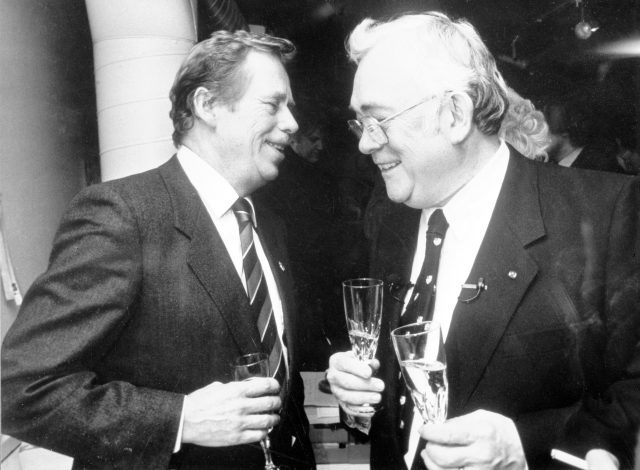

Václav Havel and writer Josef Škvorecký, photo from Aktuálně.cz
Josef Škvorecký (1924 – 2012)
Nominated for the Nobel Prize in 1982, Škvorecký was a prolific and prominent writer on the postwar Czech literary scene. He is best known for his novels and stories, but he also wrote essays, translated works by authors such as Faulkner and Hemingway into Czech and worked as a university professor in Toronto, where he settled after fleeing Czechoslovakia during Communism. Along with his wife Zdena Salivarová, he founded one of the most influential publishing houses, specializing in literature by dissidents, ’68 Publishers in Toronto. In his first novel, The Cowards, he introduced the character who would feature in many of his literary creations, Danny Smiřický, a young man with a passion for jazz and girls. The book takes place in a fictional town mirroring Škvorecký’s hometown of Náchod at the end of World War II. In another novel, The Miracle Game, Danny turns up again, this time amidst the political events of the 1950s and 1960s. In The Engineer of Human Souls, Danny is a university professor in Toronto. Life as an expat, the trials and tribulations of living under Communist rule and the magic of jazz are themes often found in Škvorecký’s works. Many of his books have been translated into English, including Miss Silver’s Past, The Swell Season, Dvořák in Love and The Bass Saxophone. He also wrote a trilogy of mysteries featuring Lieutenant Borůvka. During 1990 Škvorecký received the prestigious Order of the White Lion award from then President of Czechoslovakia, Václav Havel.
The Three Kings – Josef Balabán (1894 – 1941), Josef Mašín (1896 – 1942) and Václav Morávek (1904 – 1942)
A major player in the Czech resistance movement during the Nazi Occupation, The Three Kings – a code name coined by the Nazis who hunted them – made significant contributions to the Czechoslovak cause from 1939 to 1942. Working for the resistance group Defense of the Nation set up by former army officers, protagonists Josef Balabán, Josef Mašín and Václav Morávek relayed information about life in the Protectorate to the Czechoslovak government-in-exile in London via radio transmitters. News often involved the movement of goods and German transports as well as political and economic events. These resistance fighters also carried out acts of sabotage by staging bomb attacks and setting fire to factories. They collected weapons for the resistance and helped with the publishing and distribution of the underground magazine V boj! as well. In addition, the three-man team helped agents escape from the Protectorate.
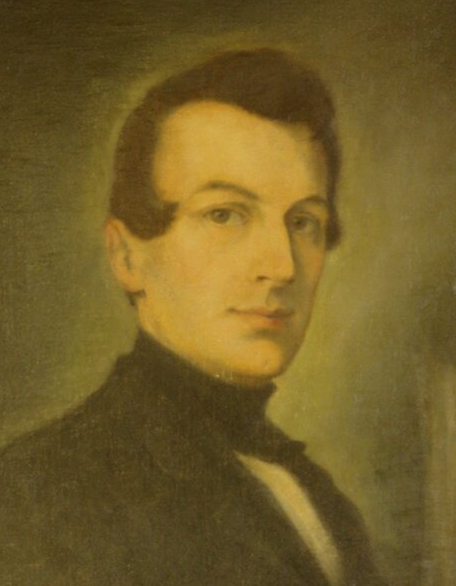
Josef Kajetán Tyl, photo from web pages of Středočeský kraj
Josef Kajetán Tyl (1808 – 1856)
This playwright, journalist, writer and actor wrote the words for the Czech national anthem, Where is my home? He served as actor, director and playwright for an amateur group who performed plays in Czech at Prague’s Theatre of the Estates, where most of the performances were staged in German. After Tyl left that theatre in 1846, he experienced the peak of his career as his collected works were published, and he received many awards. A key player in the Czech National Revival, Tyl got involved in politics during the revolutionary year of 1848, when the Czechs voiced their desire for independence from the Habsburgs. Many of his 20 plays are still performed today. They basically involve three themes. Some focus on everyday life in Czech society while others portray historical events in the Czech lands. Still others can be described as fairy tales.
Petr Vok of Rožmberk (Rosenberg) (1539 – 1611)
The last of the prominent Rožmberk (sometimes called Rosenberg) dynasty, Petr Vok of Rožmberk created magnificent Renaissance chateaus in Bechyně and Třeboň and influenced the development of Český Krumlov Castle, where he also spent his early childhood. His collection of artifacts and instruments was vast and extremely impressive. A Protestant nobleman during the Catholic Habsburg era of the Holy Roman Empire, he became the non-Catholic authority in the Czech lands.
Wenceslas (Saint) (ca. 907 – 935)
The first Czech saint and the patron saint of the Czech state, Wenceslas (Václav in Czech) served as duke of Bohemia from 921 until his death in 929 or 935. Although he died young, this martyr’s accomplishments were many. He had numerous churches built in Bohemia and was revered as a pious, moral, educated and intelligent man who promoted the Christian faith and took care of the poor, the sick, the widowed and the orphaned by doing good deeds. He founded the rotunda of Saint Vitus at Prague Castle. Wenceslas was executed at the site of the present-day city of Stará Boleslav, on the orders of his younger brother, Boleslav, who took over the Bohemian throne. At the top of Prague’s Wenceslas Square, there is a statue depicting the saint on horseback. It was constructed in 1912.
Wenceslas III (1289 – 1306)
When Wenceslas III was murdered on August 4, 1306, it marked the end of the male line of the legendary Přemysl dynasty of rulers of Bohemia, a dynasty that dated back to the ninth century. The house of Luxembourg took control of the Bohemian throne in 1310. The teenage Wenceslas III ruled Hungary, Poland and Bohemia for a brief period, and his tenure on the throne was punctuated by much friction with Hungary and Poland. It is not known who murdered him while he was resting in a former deanery in Olomouc, Moravia. Wenceslas III had not yet turned 17 at the time of his death. Over the centuries his skeleton was lost.

Jan Werich and Jiří Voskovec, photo from ceskatelevize.cz
Jan Werich (1905 – 1980)
Actor, dramatist and screenwriter Jan Werich dazzled the public in both film and theatre productions. The comic duo of Werich and Jiří Voskovec dominated Czech avant-garde theatre between world wars. The man with the deep voice, the chubby cheeks and glowing smile of Santa Claus continued to be a major influence on Czech culture after World War II until his death in 1980.

Statue of Jan Žižka in front of National Monument in Vítkov, Prague, photo from Alamy
Jan Žižka of Trocnov and the Chalice (1360 1424)
Jan Žižka is one of seven military commanders in history never to lose a battle and one of the greatest leaders in military history. His Hussite army was the first to use field artillery in battle, as Žižka employed unique and ingenious tactics. He brought armored wagons on which there were cannons and muskets into battles and was very successful. In the Battle of Kutná Hora during 1421 he defeated the Holy Roman Empire and Hungary. He led the Taborites during the Hussite Wars. Even going blind did not hinder him from leading his troops into battle.
Tracy A. Burns is a writer, proofreader and editor in Prague.