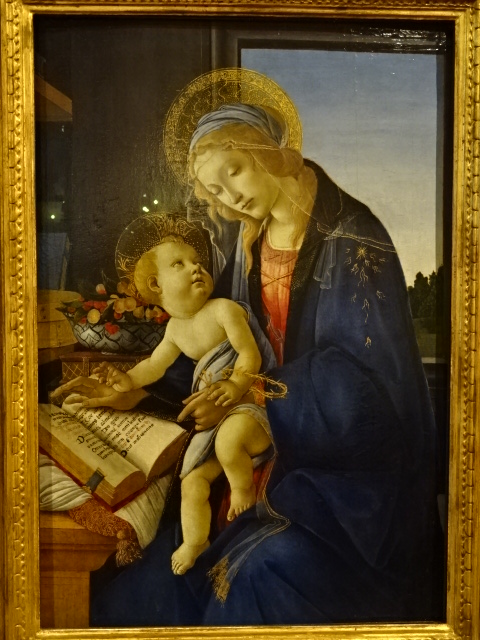
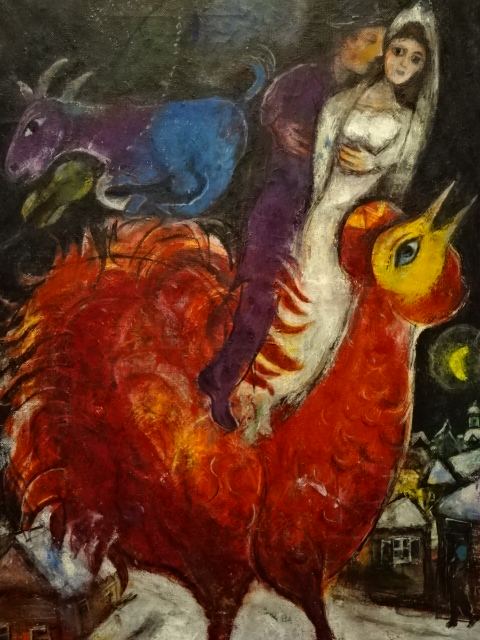I admired Marc Chagall’s works at the Albertina venue in Vienna, Austria during late October of 2024. I have always loved going to exhibitions in the Albertina. I recalled a comprehensive show of works by Durer at that venue some years ago. A long-time fan of Chagall, I loved his use of bright colors and atmosphere of playfulness in his paintings that had a dreamy, fantasy-filled quality. I was enamored with his mastery of color to express various emotions and to create new worlds. I loved his renditions of Paris, the Eiffel Tower often dominating his creations.

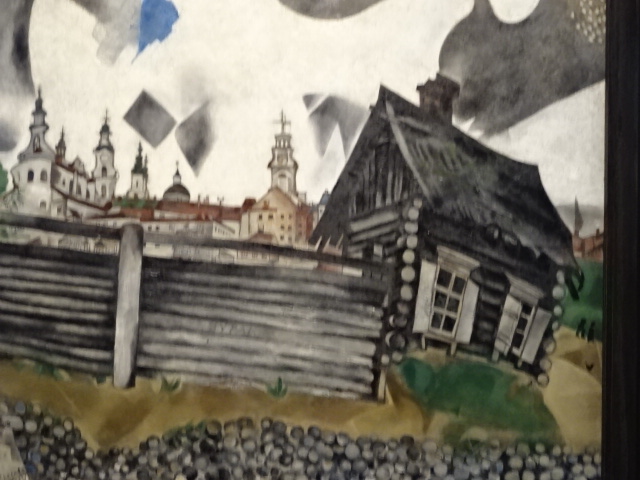
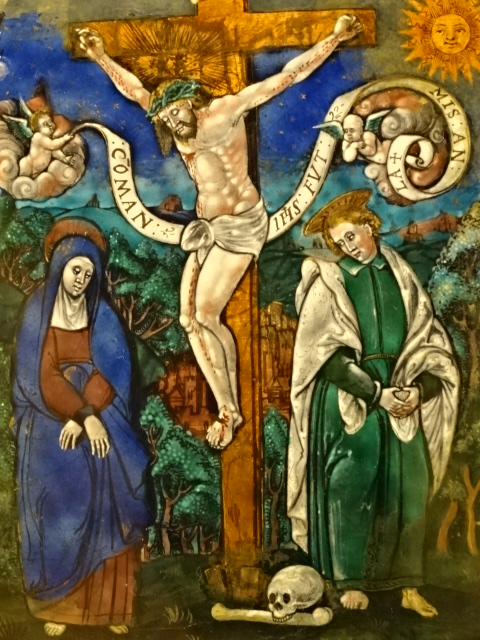
Before this show I hadn’t realized how strongly his Jewish background had influenced his art. Chagall’s paintings were punctuated with Jewish folklore and motifs. I saw a painting of a synagogue and portraits of rabbis, for instance. Many paintings boasted biblical themes. I also hadn’t realized how often he had rendered his hometown, both sadness and joy intermingled in the memories. His yearning to return to his hometown was extremely visible in his art.

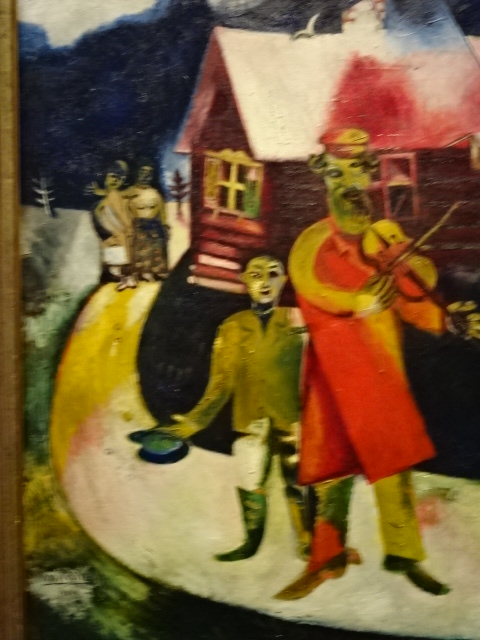
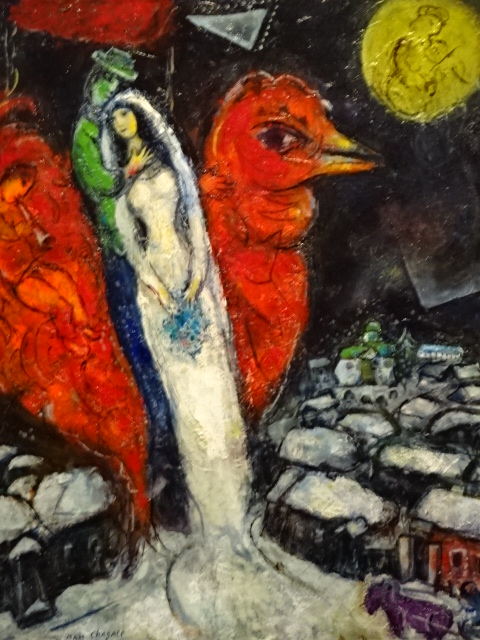
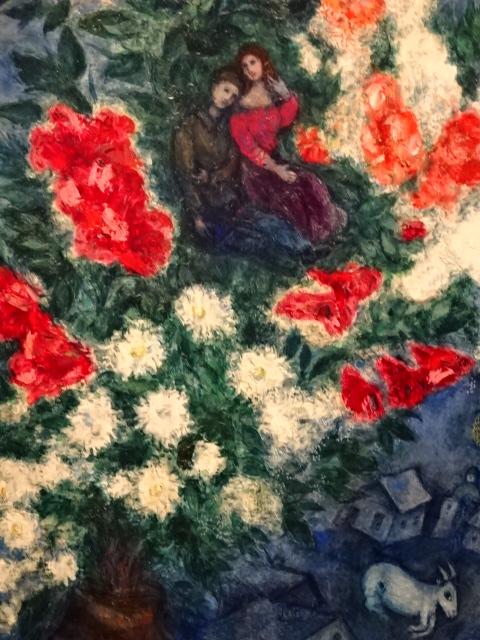
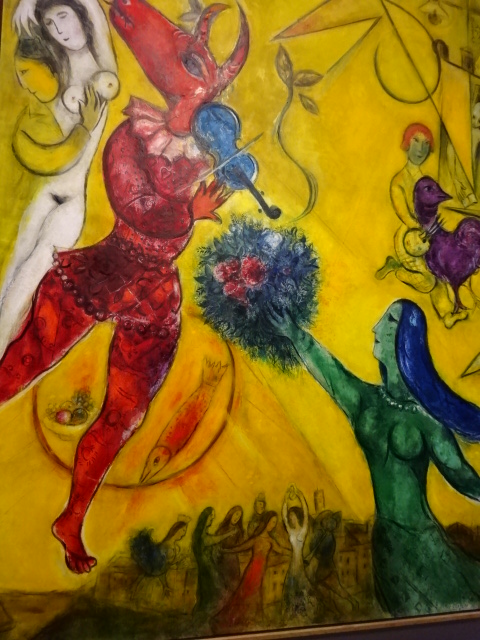
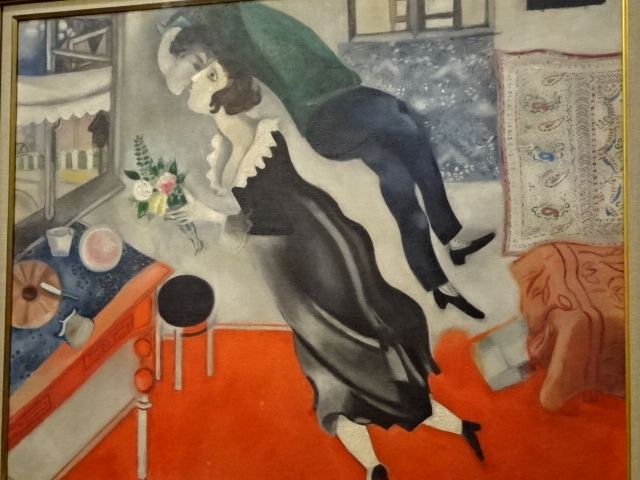
The symbolic nature of his artistic creations also enamored me as I noted the many violinists, animals, half-human creatures, wooden houses, circus characters, roosters and floating married couples as well as beautiful floral arrangements. Because I had visited an exhibition in Prague’s Wallenstein Riding Stables about the interwar years of the École de Paris movement, I knew he had been associated with that era during his Paris sojourn.

The exhibition allowed me to become better acquainted with the artist’s life. Marc Chagall (1887-1985)was born as Moishe Shagal on July 6, 1885 into a Hasidic Jewish family in Vitebsk, located in today’s Belarus. During the late 19th century the town was situated in the Russian Empire. His impressive, varied resume includes paintings, drawings, book illustrations, ceramics, prints, tapestries, stained glass and stage sets, but this vast exhibition focused solely on his paintings.

While he spent World War I in his hometown, he went to Paris before the war broke out, moving there in 1910 when he was 23 years old. In France he made friends with Guillaume Apollinaire, Ferdinand Léger and others creating avant-garde works. He often depicted Jewish themes and also evoked Paris in many paintings. During World War I, back in Vitebsk, he married Bella and held exhibitions in Russia as the war made it impossible for him to leave the empire. He founded an arts college in his hometown, too. However, he was in dire financial straits during the Russian Civil War. After World War I, much of his work was Moscow-based.

Following the Bolshevik Revolution, he moved to Paris for the second time, but fled during World War II after the Germans took control of France. The Nazis in occupied France took away Chagall’s French citizenship, and he and his wife were arrested. However, with the help of others, he and his wife found a way to escape to the USA. He felt like an outsider and didn’t speak English.

While he was in New York City, tragedy struck his hometown of Vitebsk, which was destroyed by the Nazis. Things would get even worse. Bela passed in1944 because it was not possible to get her any penicillin. It was no surprise then that Chagall’s late spouse appeared in many of his paintings. In 1948, though, he returned to Paris, and there his paintings focused on Jewish themes and his yearning for the existence of his hometown. Also, he would marry two more times.

He devoted much time to other fields as well. Some of his accomplishments included creating stained glass decoration in the cathedral in Reims and at the Art Institute in Chicago. He also made stained glass adornment for places in Switzerland and Israel. He became even better known for his ceiling painting of the Paris Opera. I remembered gazing in awe at this ceiling several decades ago. It was an experience I will never forget, even though I saw it so long ago. He also made sculpture and ceramics as well as tapestries.

Chagall died at the age of 97 on March 28, 1985 at the age of 97. He is buried with his third wife in a cemetery in Saint Paul-de-Vence, located in the Provence region.
Tracy A. Burns is a writer, proofreader and editor in Prague.