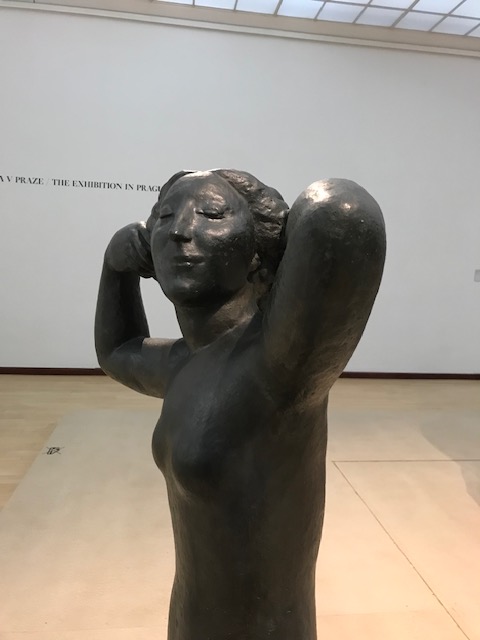
Josef Čapek, The Sailor
A long-term temporary exhibition, the First Republic art exhibition in Prague’s Trade Fair Palace showcases mostly Czechoslovak paintings and sculpture from 1918 to 1938, when Czechoslovakia was a democratic state under the guidance of President Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk. Czechoslovakia was founded in 1918, and Masaryk, who had been living in exile, was welcomed back into the Czech lands with much celebration and fanfare. The Munich Agreement, signed in September of 1938, proved a dark and dismal event in Czechoslovakia’s history, as the country ceded its German-minority Sudetenland to Hitler’s Third Reich. On March 15, 1939, the Nazis would march into Prague, and Hitler would set up the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, starting a horrific chapter in Czech and Central European history.

Josef Čapek

Myslbek
The exhibition examines the flourishing of art in the various cultural centers of Czechoslovakia, first and foremost in Prague but also in Brno, the capital of Moravia. In Slovakia the cultural hubs were located in Bratislava and eastern Košice. Zarkarpattia was a section of Czechoslovakia from 1920 to 1938, and its city of Užhorod was the setting of some intriguing exhibitions. The exhibition not only features Czech art but also Czech-German production and Slovak artistic endeavors.

Antonín Slavíček, House in Kameničky, 1904
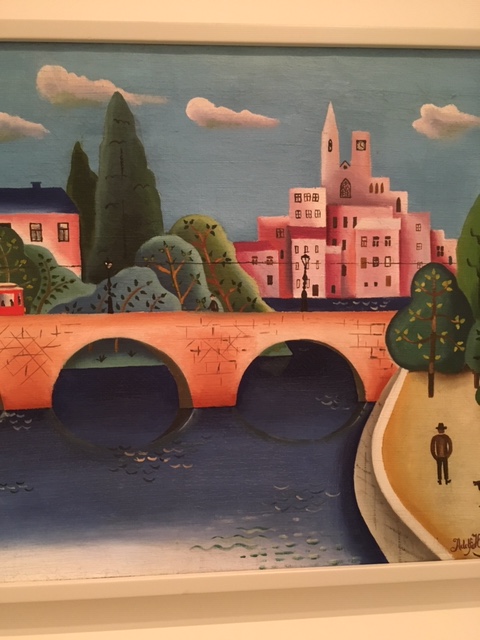

Adolf Hoffmeister, Bridge, 1922

Bohumil Kubišta, Quarry in Braník, 1910-11
Some of the Czech and Slovak artists whose works shine in the exhibition are Antonin Slavíček, Max Švabinský, Josef Čapek, Václav Špála, Jan Zrzavý, Jan Preisler, Ľudovít Fulla, Martin Benka, Bohumil Kubišta and Josef Šíma as well as Toyen and Jindřich Štyrský. The German and Austrian artists represented include August Bromse, Max Pechstein and Oskar Kokoschka, a favorite of mine.
Sculpture by Auguste Rodin, Paul Cezanne, House in Aix, 1885-87
French art from the 19th and 20th century is also on display as the Mánes Association in Prague held an important exhibition of French art at the Municipal House during 1923. The dynamic renditions of Monet, Matisse, Renoir, Van Gogh, Seurat, Gauguin, Rodin, Rousseau and others are in the limelight, too. The paintings of Georges Braque and Pablo Picasso explore Cubist tendencies.
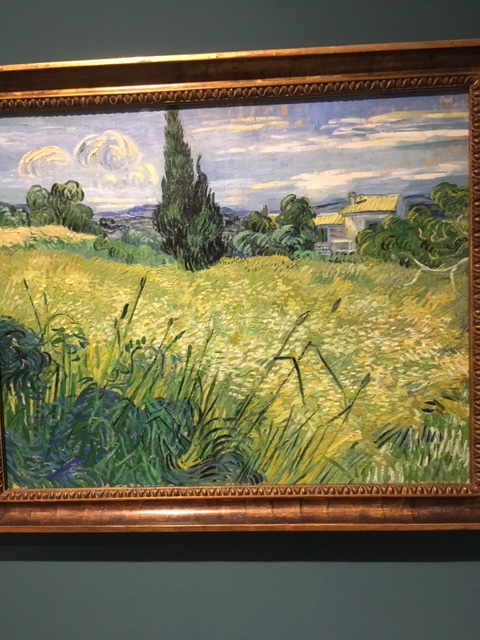

Vincent Van Gogh, Green Wheat Field, 1889

Henri Rousseau, Self-Portrait – Me. Portrait – Landscape, 1890
Paul Cezanne

Georges Seurat, Harbor in Honfleur, 1886
I was particularly impressed by the works of a Czech artistic group called the Obstinates, established at the Municipal House. It included artists who spent World War I in Prague. I liked to eat chicken with potatoes at the Art Nouveau Municipal House, and I sometimes would imagine what it had been like for those artists to discuss their ideas and theories of art there. Three of my favorite Czech painters belonged to this group of avant-garde art that had traits of Cubism and Expressionism: Josef Čapek, Špála and Zrzavý. The Municipal House at that time was one of the most prominent exhibition spaces. It still houses art exhibitions and nowadays also includes a concert hall.
On right: Jan Zrzavý, Lady in the Loge, 1918
I also tried to imagine the avant-garde Devětsil group having its first exhibition during 1922 at the Union of Fine Arts in the Rudolfinum, now the main concert house for the Czech Philharmonic. I have attended many concerts there, even seeing my favorite violinist Joshua Bell on its stage twice. I wondered what it had been like to see the works of Karel Teige, Adolf Hoffmeister and Štyrský in that majestic building during 1922 and 1923.

Jindřich Štyrský, The Puppeteer, 1921
My favorite painting in the exhibition was called “Woman with a Cat” by František Zdeněk Eberl. I am a cat fanatic, and the woman in the painting is holding her cat on her shoulder so lovingly. You can sense that the cat is an important part of her family just as my Šarlota Garrigue Masaryková Burnsová is for me. (My cat is named after President Masaryk’s wife, the First Republic’s First Lady of Czechoslovakia.)

František Zdeněk Eberl, Woman with a Cat, around 1929
The exhibition also highlighted the importance of the Mánes Association of Fine Artists, which had been established by Prague students in 1887. It had many functions, organizing exhibitions and lectures as well as editing magazines, for instance.


Karl Schmidt-Rottluff, Village Square, 1920
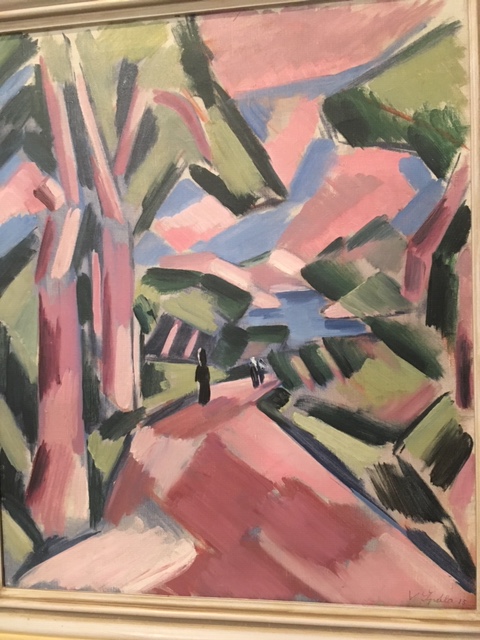

Václav Špála
V
Vincenc Beneš, Behind the Mill in Písek, 1928
There were African art relics in the exhibition as well. I thought of Josef Čapek, who had been greatly influenced by African art. The exhibition informed museumgoers that Emil Filla’s paintings had been on display with African art at the Mánes in 1935. Filla had a strong interest in non-European art and was an avid supporter of the surrealist trends in Czechoslovakia.

Another significant exhibition space during that era was the Dr. Feigl Gallery. Hugo Feigl made quite a name for himself as a private gallery owner. The exhibitions he put together did not only display Czech art but also highlighted Czech-German, Jewish and artists from around the world. He did not only organize exhibitions at his own gallery. One art show that interested me was Feigl’s exhibition of German and Austrian artists who had come to Prague as refugees, fleeing Hitler as the dictator amassed more and more power. Oskar Kokoschka, one of my favorite painters, was a refugee who had made his home in Prague. I loved his view of the Charles Bridge and his view of Prague on display. They captured the magical spell of Prague using avant-garde techniques.
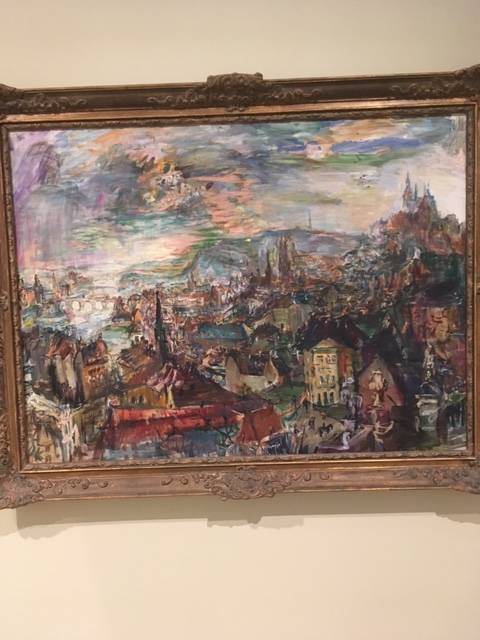

Oskar Kokoschka, Prague – View from Kramář’s Villa, 1934-35
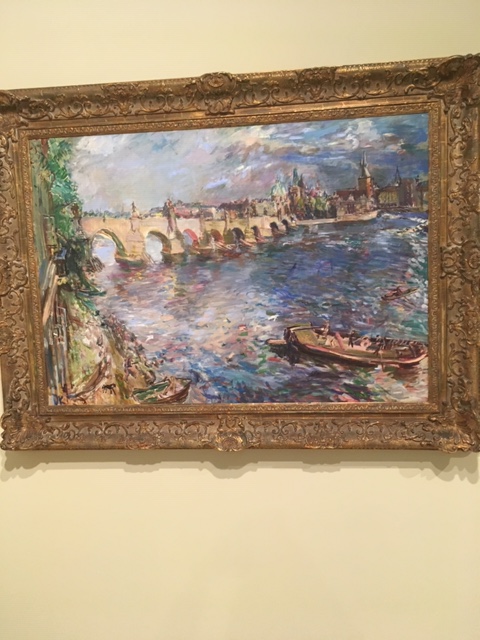

Oskar Kokoschka, Prague – Charles Bridge, 1934

August Bromse, Descent from the Cross, before 1922
In 1937, Feigl even organized a daring exhibition of German Expressionist works from a German collection of which the Nazis were by no means fans. This exhibition encouraged people to protest against an exhibition in Munich, one that glorified the Nazi regime with its display of Nazi-approved art.
Václav Špála, By the River – Vltava near Červená, 1927, sculpture by Otto Gutfreund
I was also enthralled by the exhibitions that had taken place in Brno, Zlín and Bratislava. I had poignant memories of all three places. I had helped out at the first international theatre festival organized by the Theatre on a String in Brno many years ago. People in Brno had been so friendly, and my Czech really improved thanks to my time spent there. I had also visited some villas in Brno and knew the city’s sights well.

Max Švabinský, In the Land of Peace, 1922
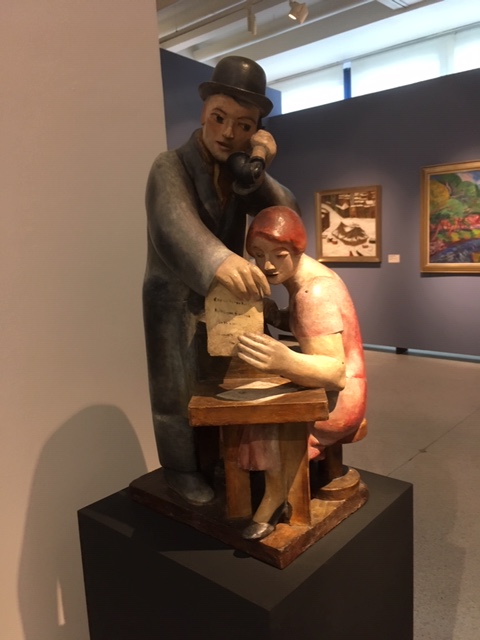

Otto Gutfreund, Business, 1923
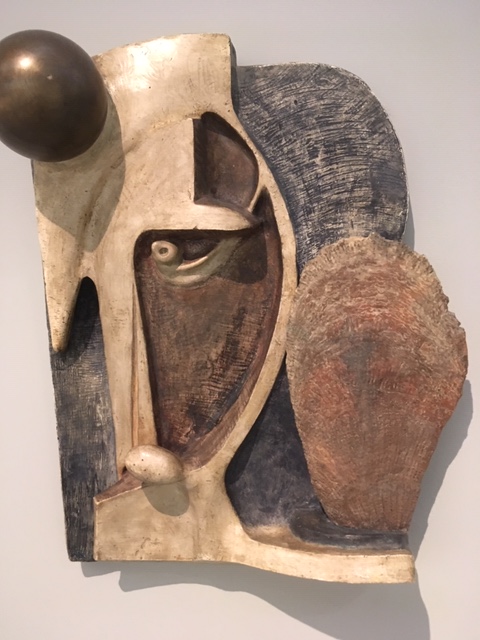

I had spent several days of one vacation in Zlín, where I had toured the fascinating Báťa shoe museum, which probably featured every kind of shoe imaginable. More than a decade ago, I had visited Bratislava once a month to help take care of my favorite Slovak writer’s grave. I had also visited the Slovak National Theatre, learning Slovak in part thanks to its performances. I loved the Slovak language and felt at peace hearing people around me speak it. I also felt this way when I heard Czech. I especially liked the works of Slovak painter Ľudovít Fulla. His use of bright colors, in his work “Balloons” for example, gave his paintings a dynamism and vitality that was unforgettable.
On right: Ľudovít Fulla, Balloons, 1930
Košice and Užhorod were featured as artistic centers, too. I had spent a lot of time in Košice during my travels to Slovakia as some of my ancestors had been from that region, and I had also used Košice as a starting point to visit other places in east Slovakia, such as Humenné and the Vihorlat. I had never been to Užhorod, which Czechoslovakia had begun to modernize during the early days of the country’s existence. I was surprised that architect Josef Gočár had designed some functionalist buildings there. I often walked by some of Gočár’s architectural achievements in the Baba quarter of functionalist individual family homes.
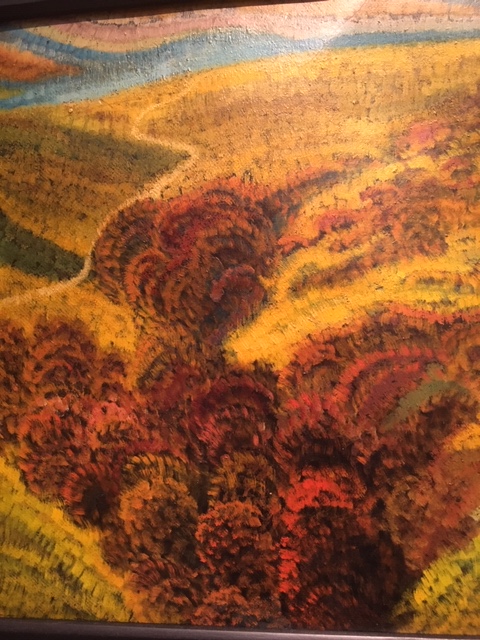

Anton Jaszusch, Landscape, 1920-24

Pablo Picasso, Still Life with a Goblet, 1922
The exhibition also informed me that between 1933 and 1938, about 10,000 refugees from Germany and Austria had officially made their way to Czechoslovakia while the number of unofficial refugees was about the same. Many significant artists came to Czechoslovakia to flee Hitler’s hold on Germany and Austria.

Caricature of Hitler, John Heartfield, Adolf the Superman: Swallows Gold and Spouts Junk, 1932
I was surprised to discover that as early as 1934 an exhibition of caricatures and humor protested Hitler’s ascent to power. It took place at the Mánes Association of Fine Artists. The caricatures were not limited to Hitler and even included some of the “good guys.” For instance, artists also poked fun at Masaryk. I was very moved by Josef Čapek’s versions of the painting “Fire,” showing a person unable to escape the dancing flames, artworks providing a stark warning about the danger of Hitler’s ideology and reign. The caricature of Hitler was chilling. Hitler’s head was perched atop a chest x-ray. His spine was made up of coins. His heart was shaped like a swastika.
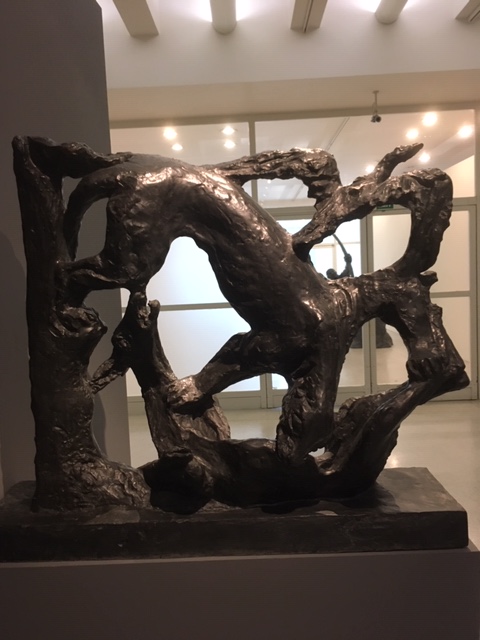

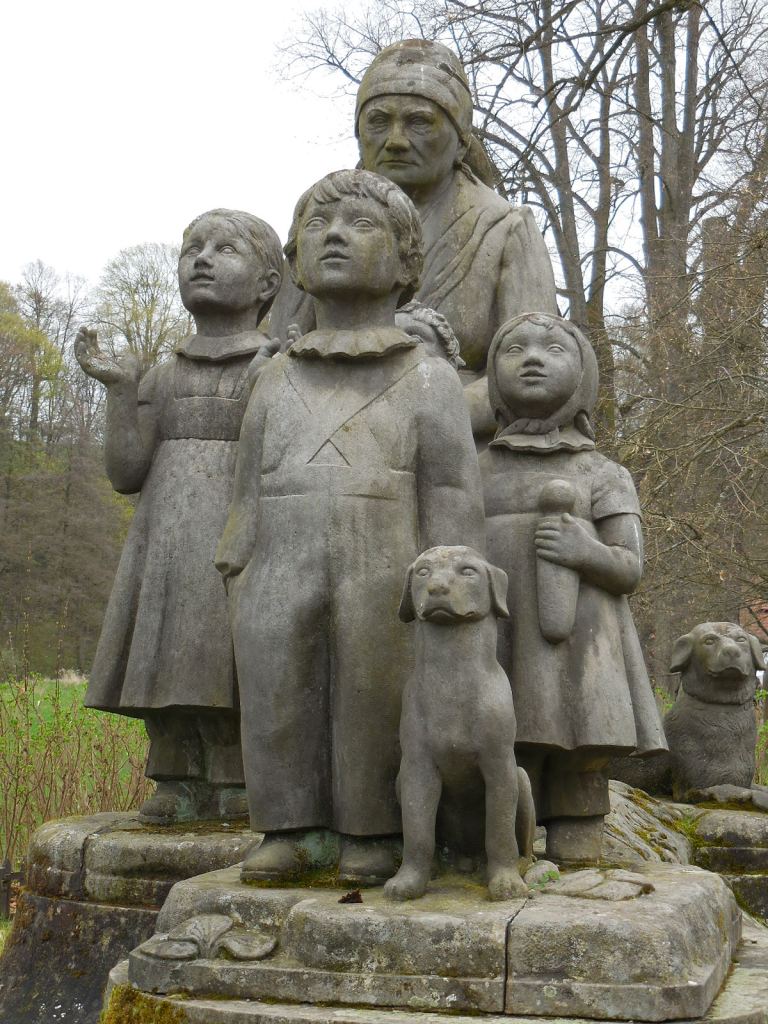
A sculpture commenting on the Munich Agreement of 1938

Josef Čapek, Fire, 1938
The exhibition ended with those works commenting Hitler’s control of the region, specifically on the Munich Agreement of 1938. While those paintings and the sculpture profoundly affected me, I preferred to concentrate on the avant-garde creations that had been featured in an artistically flourishing democratic Czechoslovakia, when artists boldly experimented with their artistic visions, during an era that I had always wanted to visit if I could go back in time. I would have loved to experience the atmosphere of the country when democracy was fresh, the state new and full of promise. Little did anyone know at its inception that the First Republic would not last long and that such a chilling chapter would follow.
Tracy A. Burns is a writer, proofreader and editor in Prague.

Furniture set from First Republic, Jan Vaněk