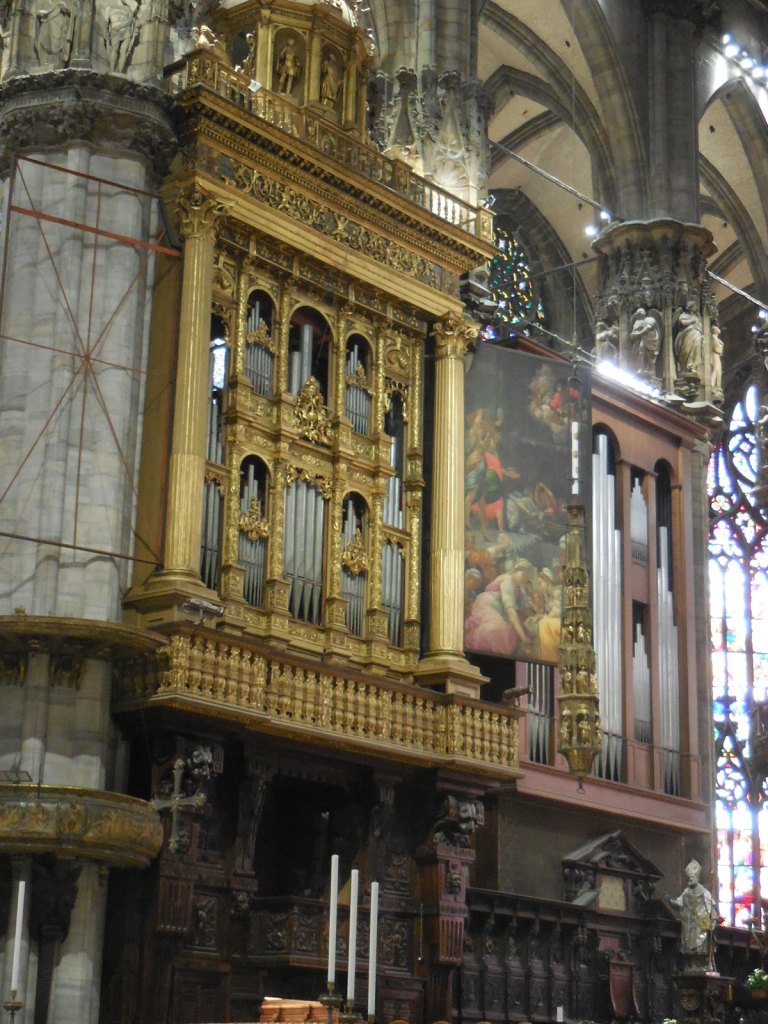
I visited Prague’s National Technical Museum for the first time in 2023, even though I have been living in Prague for more than 25 years. I am not a big technology fan and didn’t think I would be very interested in the exhibits.
I couldn’t have been more wrong. The museum includes sections on astronomy; chemistry; sugar and chocolate; transportation; printing; household items; photography; the measurement of time; architecture, civil engineering and design; metallurgy and mining, for instance. A TV studio used by Czech television from 1997 to 2011 allows visitors to sit behind a news desk and see how the TV technology works. A mock mine from the 1950s makes up another exposition. In this post I will concentrate on my two favorite parts – transportation and architecture, civil engineering and design.
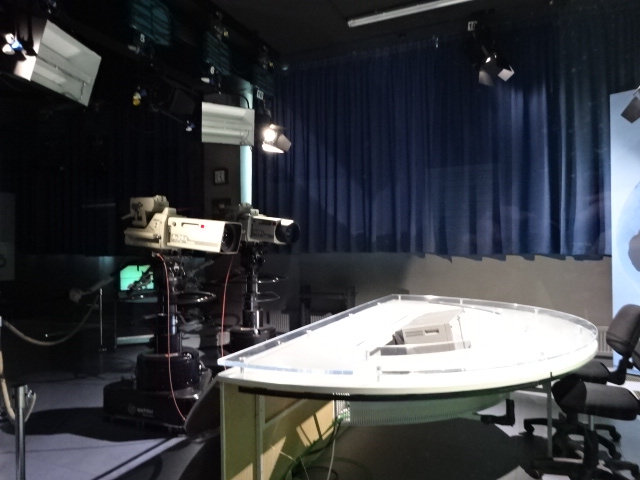

Television studio in National Technical Museum
The history of the museum itself is intriguing. Vojtěch Náprstek, a Czech patriot and world-traveler, established the Czech Industrial Museum in 1862. While many exhibits from this museum are now in the Náprstek Museum, some pieces in the collection found their way to the National Technical Museum, which was founded in 1908. Two years later, the museum opened in Prague’s Schwarzenberg Palace near the Castle. After Czechoslovakia was founded in 1918, it moved to the Letná district of Prague, where it is situated today. Construction took place from 1938 to 1941, but, during the Nazi Occupation, the building was used as the ministry of the postal service. After World War II, the museum was located on Letná again, though it was not allocated the entire building. In 1951, new expositions were created, such as transportation, mining, astronomy and photography.
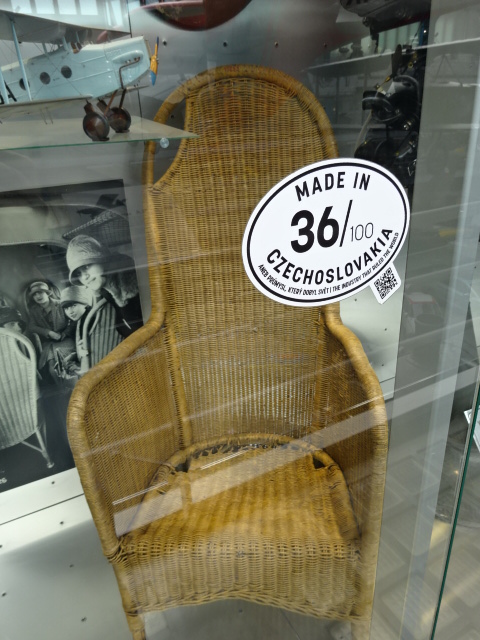

Wicker seat for passengers from Czechoslovak Aria BH-25 airliner, 1920
After the Velvet Revolution that had brought democracy to Czechoslovakia, the museum was able to utilize the entire building. However, there were difficult times ahead. During the 2002 floods, the museum’s depository in the Karlín district was heavily damaged, and some of the artifacts were ruined. Reconstruction started in 2003. In 2011, five expositions were opened. Still, construction wasn’t totally finished until 2013.

Masaryk’s presidential car

Zigmund and Hazelka’s car in which they traveled throughout Africa and South America
The main hall housing the transportation section is vast and overwhelming. Automobiles, a train dining car, planes, a boat, motorcycles and bicycles all make up the breathtaking exhibition. I liked the Tatra 80 car from 1935, the automobile of the first president of democratic Czechoslovakia, Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk, because I was interested in the First Republic era from 1918 to 1938. I also was excited to see the Tatra 87 car of world travelers Jiří Hanzelka and Miroslav Zigmund. They traveled around Africa and South America in that car from 1947 to 1950 and did more than 700 reports for radio broadcasts about their trips. The two had been the dynamic duo of travel: They visited more than 100 countries. They also made films, mostly documentaries, and wrote books together.

The dining car of Habsburg Emperor Franz Joseph I and later of President Masaryk
I was enamored by the dining car of Habsburg Emperor Franz Joseph I, which in 1923 became part of Masaryk’s presidential train. When President Edvard Beneš returned to his homeland from exile after the war in 1945, this dining car was part of his train. The dining car was put out of commission in 1959.
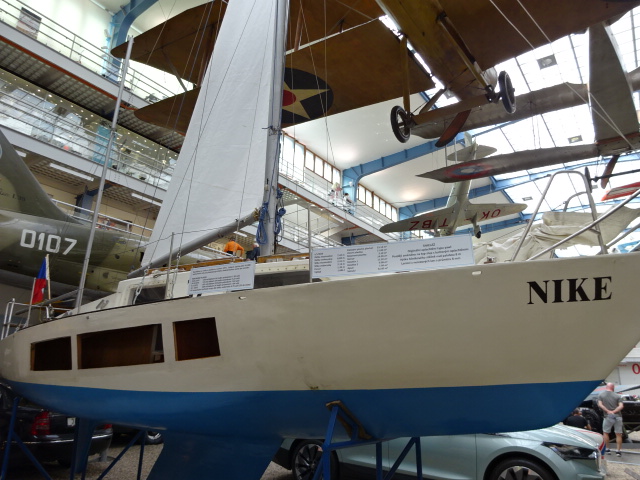

A sailing boat called Nike was on display, too. Czech Richard Kankolski had sailed around the world in it during 1972, and, at that time, it earned the distinction of being the second smallest boat to sail around the world.
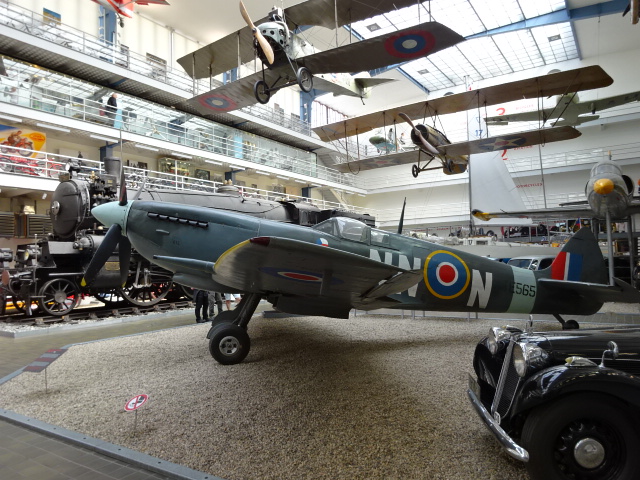

British Spitfire
Three planes that saw action in World War I also are displayed, including an American one. Dating from 1911, the plane manned by the first Czech pilot Jan Kašpar is part of the exhibition. I was drawn to the British Spitfire that members of a Czechoslovak squadron of the RAF had flown during World War II.
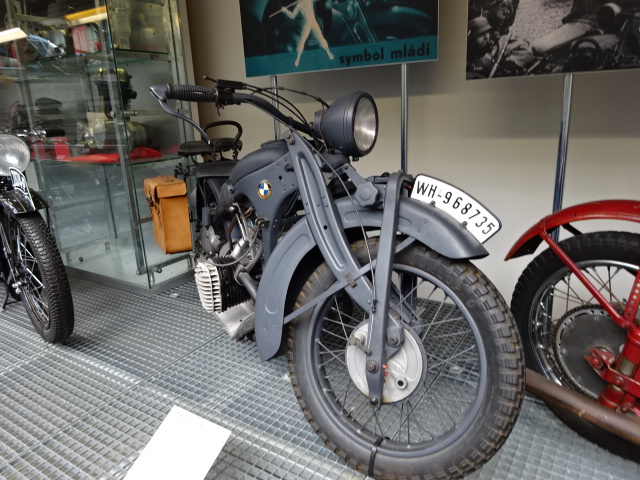

Germans drove this kind of motorcycle when they occupied Czechoslovakia in 1939.
I was very interested in the various bicycles and motorcycles, too, even though I vow never to ride either of them. A bamboo-made Slavia bike hails from 1905. The BMW R11 from 1932 caught my undivided attention because the Germans had driven these motorcycles when they occupied Czechoslovakia on March 15, 1939. I tried to imagine seeing so many of these motorcycles at Prague Castle with the flag of the Third Reich fluttering from the flagpole. The very thought was chilling.
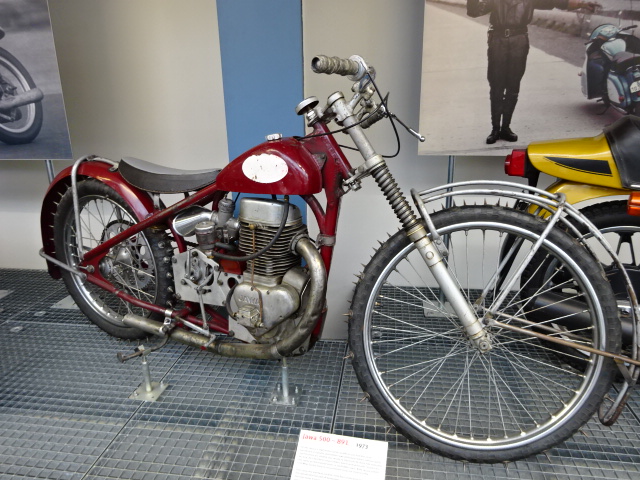

Milan Špinka’s bike
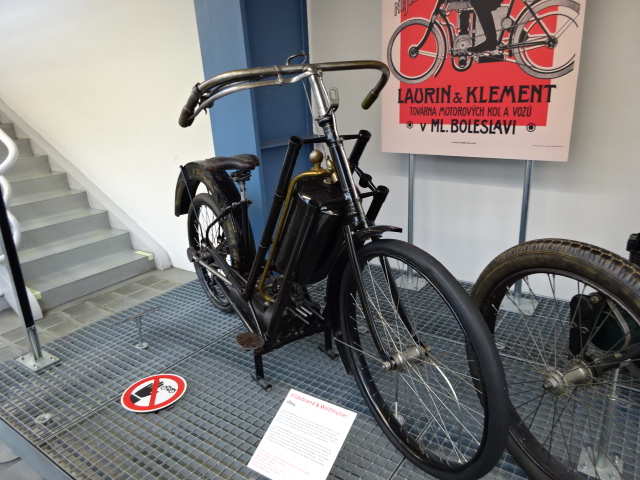

The first series-manufactured motorcycle in the world
I also saw the Jawa 500 – 891 from 1973. While the Soviet Union had excelled on ice speedway competitions, this is the motorcycle on which Czech Milan Špinka defeated the USSR in the world championships of 1974. Another motorcycle that interested me was the Hildebrand & Wolfmuller from 1894. It was the first series-manufactured motorcycle in the world. The one on display is the first motorcycle manufactured for the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
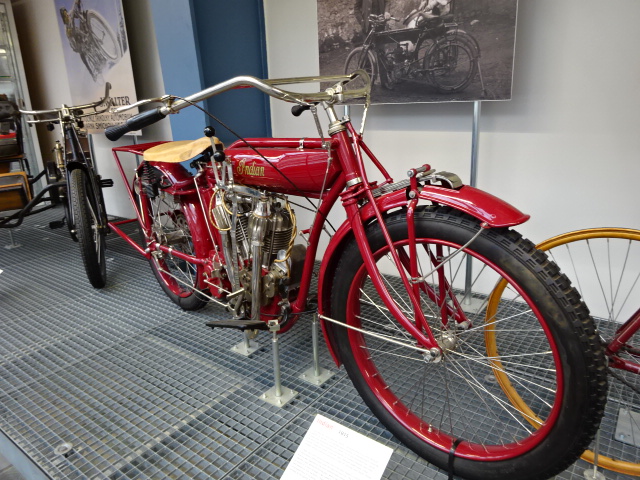

Indian brand, 1915, manufactured in America

Czechoslovak observation balloon, 1934
The architectural part of the museum covers the developments in the Czech lands from the second half of the 19th century to the present. Styles of historicism, secession, cubism, constructivism, functionalism and socialist realism as well as modern works are all represented. I loved the architectural models, especially those of villas in Prague, the Czech Pavilion at Expo 58 in Brussels and the Czechoslovak exhibition pavilion at the World Arts and Technology Exhibition in Paris during 1936. I loved to take walks through the villa-dotted sections of Prague’s Baba, Ořechovka and Hanspaulka quarters. In this museum, I saw models of famous villas in the Hodkovičky, Podolí and Troja districts of Prague, for instance.
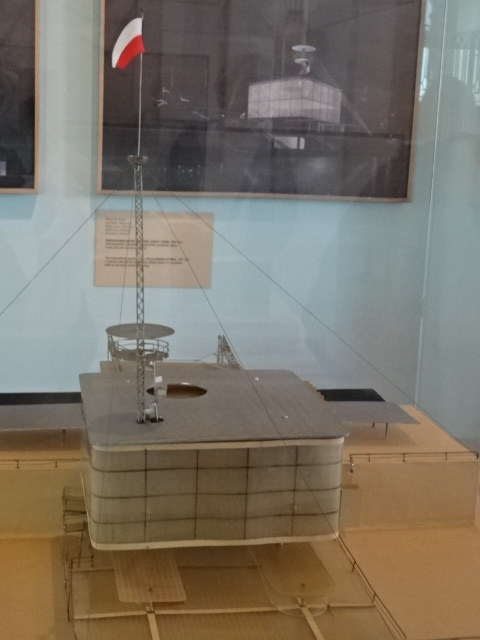
Czechoslovak World Arts and Technology pavilion, Paris, 1936

Director Martin Frič’s villa in Hodkovičky, 1934-35
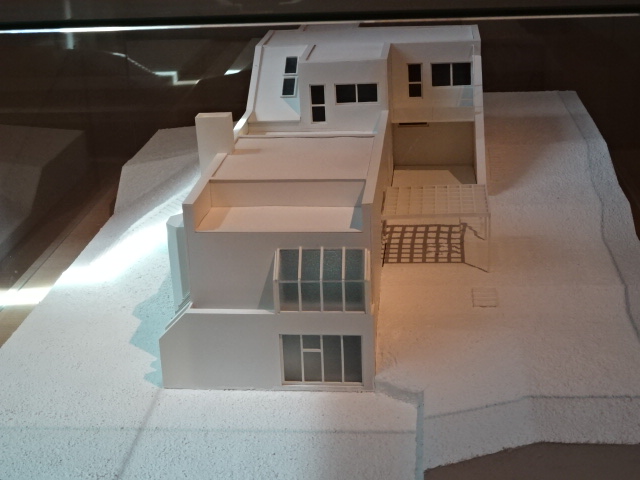
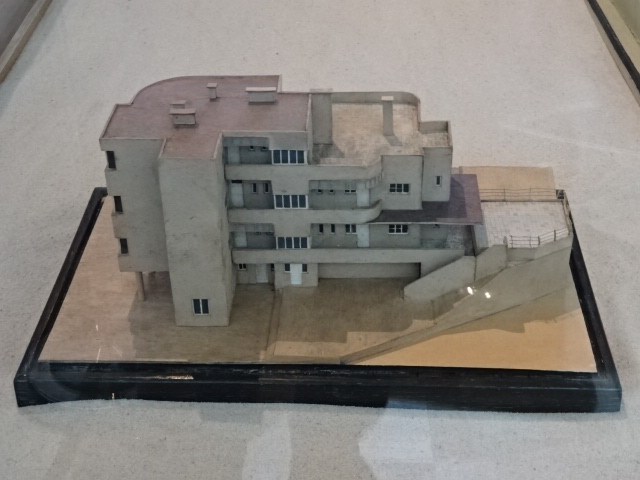

Top: Stýblo’s villa in Podolí quarter of Prague, 1935-36, Bottom: Villa of film director Věra Chytilová in Troja quarter of Prague, 1970-75
I liked the model of the column with lantern in front of Our Lady of the Snows Church in Prague because it was unique, Cubist in style. I also took notice of the Cubist Petrof BB upright piano. The model of the television transmitter and hotel on Ještěd Hill in Liberec brought back memories of the magnificent views from the observation point at the restaurant and hotel. Some models showed off designs by masterful Czech architect Jan Kotěra, including the East Bohemia Museum in Hradec Králové, which had extremely impressed me about a month previously, and the reconstruction of Saint George’s Church in Doubravka near Pilsen in west Bohemia. The museum in Hradec Králové was constructed from 1906 to 1913 while the church hails from 1899. Architectural plans and photography rounded out the exposition.
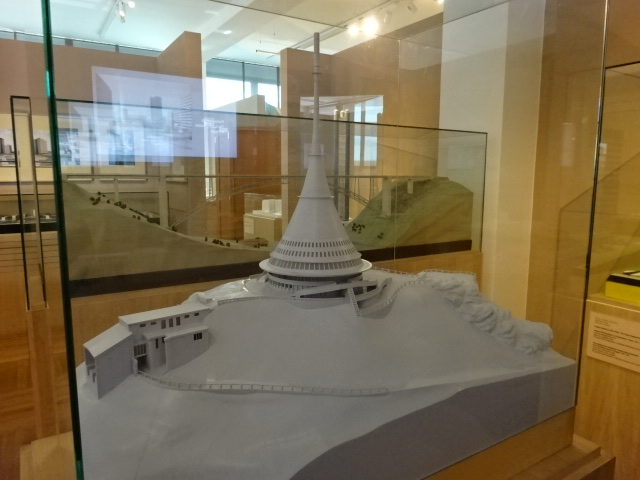
Ještěd Hill Hotel and Restaurant
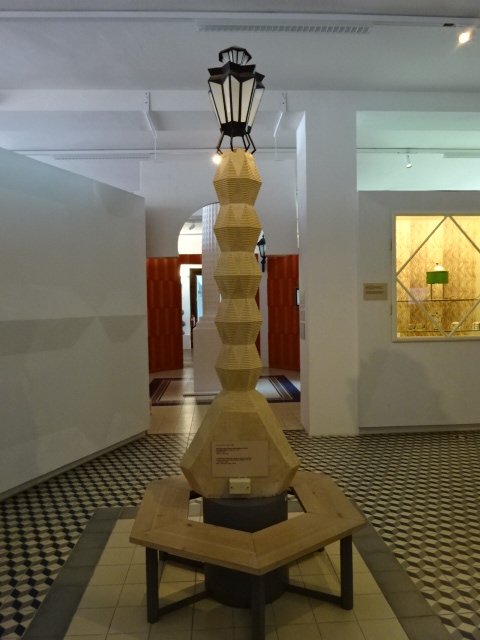


Cubist column in front of church – top photo, Cubist piano – bottom photo
I was glad I had finally visited this museum that offers valuable insights into the technical world. The main hall with various exhibits of transportation was amazing, and my interest in architecture compelled me to take a close look at the exhibits in that section. Overall, it was a day well spent.
Tracy A. Burns is a writer, proofreader and editor in Prague.

Museum of East Bohemia designed by Jan Kotěra
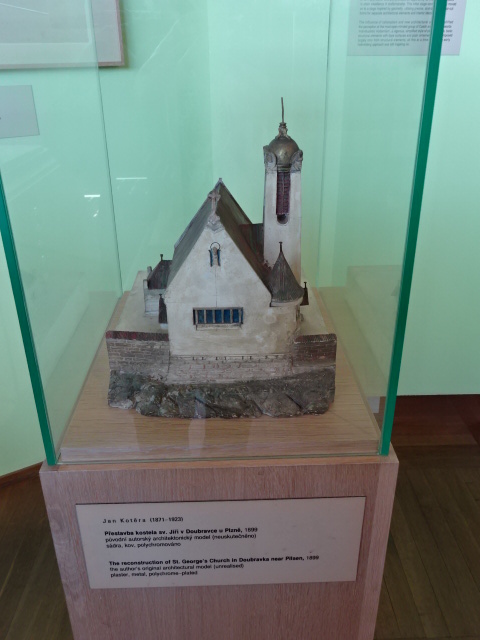

St. George’s Church designed by Jan Kotěra